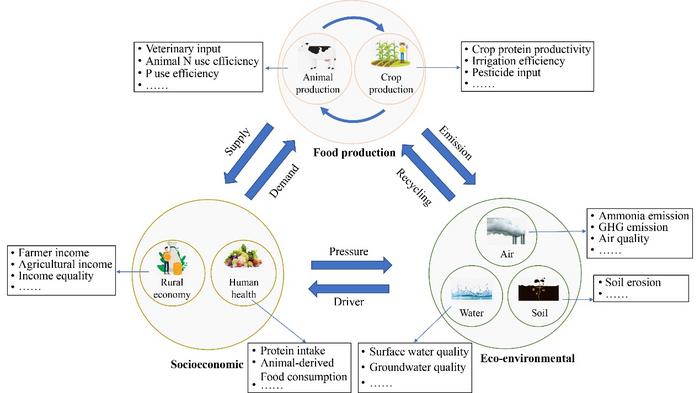
Over the past few decades, the Green Revolution has brought about significant increases in crop yields but has also led to environmental issues. Following its own Green Revolution, China has successfully met the needs of its vast population but is also facing challenges such as soil degradation, pollution, and resource depletion. The initiative for Agricultural Green Development (AGD) offers a pathway towards sustainable development, necessitating a balance between economic growth and environmental protection. To achieve this goal, China needs to implement comprehensive measures, including optimizing resource utilization, reducing emissions, and improving food quality.

Credit: Haixing ZHANG, Yuan FENG, Yanxiang JIA , Pengqi LIU , Yong HOU, Jianbo SHEN, Qichao ZHU, Fusuo ZHANG
Over the past few decades, the Green Revolution has brought about significant increases in crop yields but has also led to environmental issues. Following its own Green Revolution, China has successfully met the needs of its vast population but is also facing challenges such as soil degradation, pollution, and resource depletion. The initiative for Agricultural Green Development (AGD) offers a pathway towards sustainable development, necessitating a balance between economic growth and environmental protection. To achieve this goal, China needs to implement comprehensive measures, including optimizing resource utilization, reducing emissions, and improving food quality.
In recent time, the team led by Prof. Fusuo Zhang and Dr. Qichao Zhu from China Agriculture University proposed one indicator evaluation system consisting of three dimensions (Socioeconomic, Food production, and Eco-environmental) and ten sub-dimensions to assess China’s level of AGD from 1997 to 2020. The evaluation results indicate that China’s agricultural transformation can be roughly divided into two stages during this period: (1) 1997–2010, the score for AGD fluctuated around 40 points, with a high proportion of low-level indicators; (2) 2010–2020, the proportion of low-level indicators decreased significantly, while the proportion of good-level indicators increased. Although the score for AGD has been continuously increasing since 1997, the overall level is still moderate, with a relatively low proportion of high-level indicators.
Furthermore, it was found that the development of the three dimensions (Socioeconomic, Food production, and Eco-environmental) was uneven over the 24-year period, with growth rates of 33.3%, 20.8%, and 19.1%, respectively. The improvement in the Socioeconomic dimension was most significant, with the proportion of low-level indicators decreasing from 70% to 20% over the 24 years, contributing to a 3.5-point increase in the total score. However, the performance of the Food production and Eco-environmental dimensions was not satisfactory. Among the ten sub-dimensions, the highest increase was observed in Agricultural Productivity, followed by Production Conditions and Resource Consumption. Economic Status and Production Efficiency stagnated, while the score for Environmental Quality decreased by 14.3%. Besides, Spearman correlation analysis revealed synergies between Socioeconomic and Food production and trade-offs between Eco-environmental and the other two dimensions. In terms of indicators, Air Quality, GHG emissions, and Ammonia emissions in the Eco-environmental dimension were significantly negatively correlated with most Socioeconomic indicators.
AGD is a crucial transformational pathway for China to achieve sustainable development, providing affordable and nutritious food and improving living standards. Since 1997, China’s evaluation score for AGD has been continuously improving, with 8.3% of indicators reaching the target level in 2020, while 63.7% of indicators remain at low or moderate levels. It is evident that China’s agricultural transformation is in the right direction. Future development needs systematic coordination among the Socioeconomic, Food production, and Eco-environmental systems to reduce imbalanced development and trade-offs.
This study has been published on the Journal of Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering in Volume 11, Issue 1, 2024, DOI: 10.15302/J-FASE-2023512.
Journal
Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
China’s agriculture green development: from concept to actions
Article Publication Date
31-Aug-2023