Over the past few decades, the world has witnessed tremendous progress in the tools used for genomic analysis. While it’s usually more common to associate these tools with the fields of biology and medicine, they have proven to be very valuable in agriculture as well. Using numerous DNA markers obtained from next-generation sequencing technologies, breeders can make genomic predictions and select promising individuals based on based on their predicted trait values.

Credit: Dr. Mai F. Minamikawa from Chiba University, Japan
Over the past few decades, the world has witnessed tremendous progress in the tools used for genomic analysis. While it’s usually more common to associate these tools with the fields of biology and medicine, they have proven to be very valuable in agriculture as well. Using numerous DNA markers obtained from next-generation sequencing technologies, breeders can make genomic predictions and select promising individuals based on based on their predicted trait values.
Various systems and methodologies aimed at improving the quality of fruits use genetic analysis. One of them consists of genetic selection (GS) and genetic prediction (GP). This modern breeding approach uses statistical models to assess the entire genetic profile of a given individual based on previously collected genomes and their associated traits. This enables breeders to make predictions about the fruit traits that will be produced in the future at the seedling stage. In contrast, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are instead focused on finding the exact genetic variants that are responsible for a particular fruit trait.
Until now, GP and GWAS have predominantly used DNA markers from a single system, and when the system in use became obsolete, it had to be re-analyzed using a more up-to-date system. However, it has been difficult to re-analyze populations for selection in fruit tree breeding that have been analyzed in previous systems, as it is not possible to re-obtain DNA from individuals discarded during selection. Thus, in a recent study published in Horticulture Research on 8 July 2024, a research team led by Associate Professor Mai F. Minamikawa from the Institute for Advanced Academic Research, Chiba University, Japan, set out to clarify whether combining apple data from different systems could lead to more accurate results when performing GP and GWAS. Other members of the team included Dr. Miyuki Kunihisa from the Institute of Fruit Tree and Tea Science, National Agriculture and Food Research Organization, Japan, and Professor Hiroyoshi Iwata is from the Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences at the University of Tokyo, Japan.
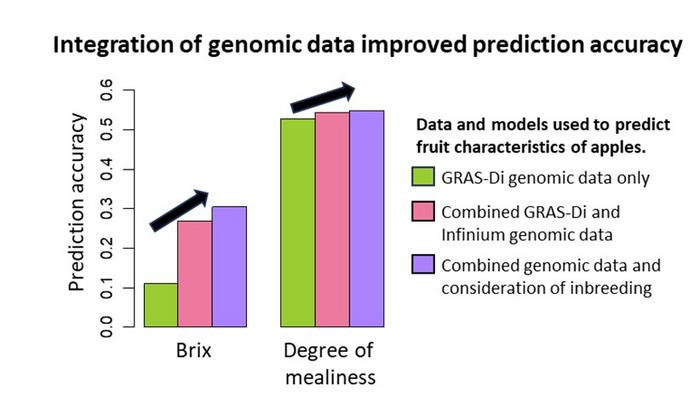
First, the researchers combined apple datasets acquired from two different genotyping systems, namely Infinium and genotyping by random amplicon sequencing direct (GRAS-Di). Then, they used these combined genotype markers to perform GP and GWAS for a total of 24 different fruit traits, including acidity, sweetness, harvest time, and solid soluble content. The team compared the performance of predictions made using models trained on either dataset alone or both combined.
The results were very encouraging; the accuracy of genomic predictions and the detection power of the GWAS system increased significantly when using the Infinium and GRAS-Di combined datasets for multiple fruit traits. This suggests there are benefits to combining data from different systems and leveraging historical data.
To push the envelope further, the researchers also trained the GP model in such a way that inbreeding effects were considered. Interestingly, these results also hinted at the combined approach performing better for certain traits, including Brix and Degree of mealiness. Still, these findings were less conclusive, as Dr. Minamikawa remarks, “Although the accuracy of GS for fruit traits in apples can be improved by data on inbreeding, further studies are needed to understand the relationship between fruit traits and inbreeding.”
Overall, the findings of this study hint at a convenient way of improving the accuracy of GS and GWAS by leveraging existing datasets. This could have many positive implications in agriculture, as Dr. Minamikawa highlights, “The challenges such as large plant size and long juvenile periods in fruit trees can be addressed by identifying superior genotypes from numerous individuals using high accuracy GS as seedling stage and detecting genetic variants for a target trait using precise GWAS.”
Let us hope further progress in this field makes the breeding of fruits more efficient and reliable so we can keep enjoying them in our diets!
About Associate Professor Mai F. Minamikawa
Dr. Minamikawa received a PhD degree from the Graduate School of Horticulture at Chiba University in 2013, where she currently holds the position of Tenure-track Associate Professor. She specializes in genomic selection, data science, and statistical and molecular genetics, with a particular focus on their application to fruit breeding. Worth noting, she is also a member of The Japanese Society of Breeding and The Japanese Society for Horticultural Science.
Journal
Horticulture Research
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Genomic prediction and genome-wide association study using combined genotypic data from different genotyping systems: Application to apple fruit quality traits
Article Publication Date
8-Jul-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.