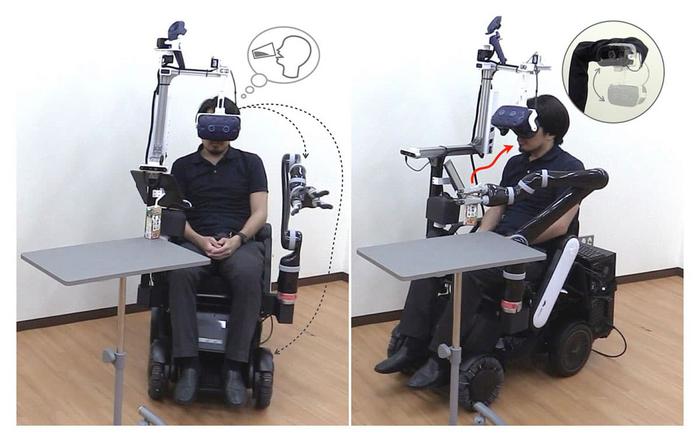
In an era where technological advancement continually reshapes the fabric of human experience, a groundbreaking development has emerged from the Institute of Systems and Information Engineering at the University of Tsukuba, Japan. The research centers around the creation of a human-collaborative robot designed to assist individuals facing the challenges of aging, illness, and neurological disorders. This initiative aims to redefine daily living for those who struggle with traditional physical and cognitive limitations, ushering in a new paradigm of independence and support through robotic intervention.
The pressing issue of declining motor and cognitive functions in the elderly and those with debilitating medical conditions has prompted an urgent need for innovative solutions. Individuals often find themselves struggling to engage in simple day-to-day tasks, leading to an increased risk of anxiety, depression, and a diminished quality of life. The newly developed robot not only interprets human intentions but actively engages with users, thereby transforming the way they interact with their environment. This significant advancement seeks to alleviate the burdens associated with caregiving and establish a more autonomous lifestyle for those in need.
At the core of this research lies an impressive technology that empowers people with challenging neurological diseases. It facilitates daily tasks without necessitating physical movement from users, harnessing the power of bioelectrical signals and gaze information to interpret their intentions. These modalities offer a revolutionary approach to human-robot interaction, allowing seamless integration between the physical and digital realms—an intersection the researchers describe as the cybernics space. This groundbreaking feature permits the robot to operate various devices and mechanisms, enhancing convenience and providing more profound assistance in everyday activities.
During rigorous testing phases, the robot successfully demonstrated its capabilities by executing essential daily movements within a simulated living environment, achieving a remarkable success rate. These trials not only validated its performance but also highlighted user satisfaction concerning the system’s usability and reliability. The implications of these findings are profound, as the technology aims to significantly diminish the need for human assistance and potentially lower overall healthcare costs for individuals requiring extensive nursing care.
As part of a broader initiative supported by the Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program in Japan, this technology incorporates diverse elements from reputable institutions and corporations. Collaborations with ARGO GRAPHICS Inc. and Silicon Studio Corporation facilitated the construction of detailed 3D models crucial to the robot’s functionality. This multifaceted effort underscores the potential of human-collaborative robots in enhancing the everyday lives of individuals while paving the way for future innovations in this field.
Moreover, the approach taken in developing this technology signifies a noteworthy shift towards personalized healthcare solutions. By focusing on multimodal vital information collection, the robot can adapt to individual user needs, further enhancing its capability to perform specific tasks based on the real-time assessment of a person’s physical and cognitive state. This adaptability not only creates a more user-friendly experience but also establishes the fundamental principle that the interface between human and robotic systems must prioritize the user’s comfort and preferences.
In essence, this research encapsulates the essence of modern robotics, where human collaboration and intelligent systems can converge to tackle some of society’s most pressing challenges. As aging populations grow and the prevalence of chronic conditions increases, the importance of developing such assistive technologies cannot be overstated. The potential benefits in improving the quality of life for countless individuals are immense, transforming what was once a daunting reality into an empowered experience.
Furthermore, the emergence of these robots epitomizes a systematic shift in how society perceives assistive technologies. Most importantly, it opens discussions about the ethical implications of robots in caregiving roles. As these machines learn to interpret human emotions and intentions, society must consider the psychological and emotional effects on individuals who interact with these robots. A careful balance must be struck between technology and human touch, ensuring that while machines provide crucial support, they do not replace the essential human connections that contribute to overall well-being.
In conclusion, the development of the human-collaborative robot by researchers at the University of Tsukuba heralds a new era in robotic assistance and cybernics. With its potential to enhance independence for individuals with motor and cognitive challenges, this innovation promises to reshape how society addresses the needs of its most vulnerable members. The implications of this research are vast, extending beyond mere assistance to redefine the relationships between humans and technology in the context of care, autonomy, and the future of living.
As we continue to witness advancements in robotics, it becomes increasingly clear that the integration of such technologies is not just beneficial but essential for future societal frameworks. The ongoing research is a significant step toward a world where individuals, regardless of their physical or cognitive limitations, can lead fulfilling lives with the aid of intelligent and responsive machines.
Subject of Research: Human-Collaborative Robot for Daily Life Support
Article Title: Development of human collaborative robot to perform daily tasks based on multimodal vital information with cybernics space
News Publication Date: 18-Mar-2025
Web References: https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2025.1462243
References: Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP)
Image Credits: University of Tsukuba
Keywords
Assistive technology, human-robot interaction, aging, neurological disorders, cybernics, robot autonomy, caregiving, multimodal information, healthcare innovation.