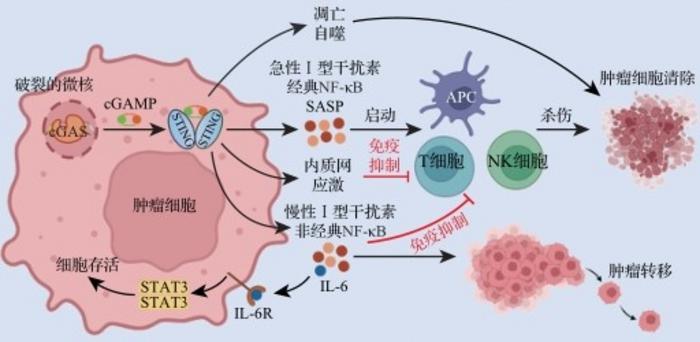
Scientists have unraveled the mechanisms of the Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway activated by micronuclei, as well as its significant effects on tumor immunity. This study illuminates how chromosomal instability, marked by micronuclei formation, plays a critical role in controlling the capacity of the innate immune system to regulate tumor progression. These findings deepen our understanding of the intricate relationship between cellular anomalies and immune responses and open new avenues for cancer therapy.

Credit: Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences)
Scientists have unraveled the mechanisms of the Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway activated by micronuclei, as well as its significant effects on tumor immunity. This study illuminates how chromosomal instability, marked by micronuclei formation, plays a critical role in controlling the capacity of the innate immune system to regulate tumor progression. These findings deepen our understanding of the intricate relationship between cellular anomalies and immune responses and open new avenues for cancer therapy.
Chromosomal instability, a hallmark of human tumors, refers to the improper segregation of chromosomes during cell division, leading to abnormalities in chromosome structure or number. This phenomenon is evident in 60%-80% of human tumor cells and is linked directly to cancer progression, recurrence, metastasis, treatment resistance, and immune escape. Understanding the molecular mechanisms by which chromosomal instability influences these aspects of cancer can significantly advance our knowledge of tumor development and identify new targets for treatment.
A recent review (DOI: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2023-0485) published on February 28, 2024, in Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences) meticulously investigates how the cGAS-STING pathway detects and responds to micronuclei and its subsequent effects on cancer. This exploration provides essential knowledge for developing and applying targeted cancer therapies.
The review details how the breaking of micronuclei, tiny nuclei encapsulated in their membranes and laden with chromosomal fragments, signals the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. This momentous event can either prompt the immune system to eliminate tumor cells or, paradoxically, aid tumor growth and immune evasion by fostering an immunosuppressive environment. The generation of micronuclei stems from cell division errors, leaving these nuclei filled with chromosomal fragments disconnected from the primary cellular processes. The rupture of these micronuclear membranes exposes DNA, engaging the cGAS-STING pathway and sparking a barrage of immune responses aimed at purging the aberrant cells, potentially stopping cancer in its tracks. Yet, the process has a dual aspect; while potentially activating the immune system against cancer, prolonged activation may create conditions conducive to cancer proliferation and dissemination.
Lead author Shen Qin remarked, “Our reviews not only illuminate the dynamic relationship between chromosomal instability and immune surveillance but also underscore the potential of harnessing the cGAS-STING pathway to develop cutting-edge cancer treatments.”
This article highlights the promise of targeting the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in cancer therapy. By discerning when this pathway supports or hinders tumor growth, researchers are poised to devise treatments that boost the immune system’s natural cancer-fighting capabilities.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31725017, 31830052); National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFA1301401).
About Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences)
Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences) has been indexed by Index Medicus (IM) since 2002, and the paper version is permanently collected by the American National Library. The full text is presented at PubMed Central (PMC) since 2022. Currently, the journal is the source journal of American Chemical Abstracts (CA), Holland Excerpta Medica (EM), The Western Pacific Region Index Medicus (WPRIM), Elsevier Scopus, and also indexed by CSCD, CJFD, CSTPCD, A Guide to the Core Journals of China. For decades, the journal has been named an Excellent Scientific and Technological Journals or the Top 100 Science and Technology Journals of Chinese Universities.
Journal
Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences)
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Role of micronucleus-activated cGAS-STING signaling in antitumor immunity
Article Publication Date
28-Feb-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.