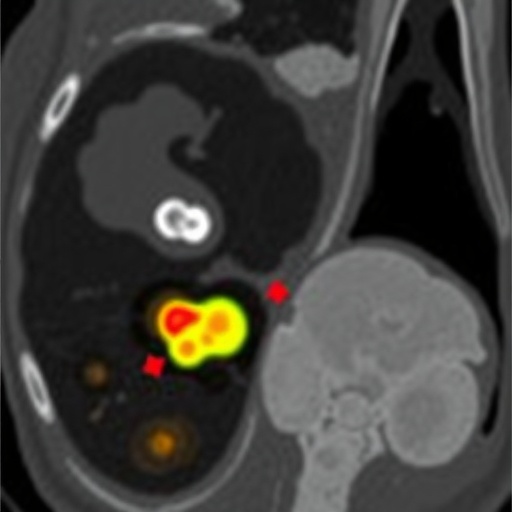
In a striking new case report, researchers led by Xiong, T., along with Wan, Q., and Yuan, C., have unveiled a compelling study highlighting an unusual presentation of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a malignant cancer that predominantly affects children. This paper contributes to the existing literature by documenting an alarming case in which the disease manifested with bone marrow metastasis. The significance of this finding cannot be overstated, as it improves our understanding of the clinical characteristics and biological behavior of RMS, a neoplasm that warrants more attention in multi-disciplinary pediatric oncology settings.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue sarcoma found in children, commonly arising from embryonic mesenchymal cells. Traditionally classified into several histological subtypes—namely alveolar, embryonal, and pleomorphic—this malignancy can present in various forms depending on its subtype and anatomical location. This case report concerns a pediatric patient who, after initial diagnosis, exhibited metastatic spread to the bone marrow, a relatively rare but devastating manifestation of the disease.
The diagnosis of RMS often involves advanced imaging modalities and a comprehensive histopathological evaluation to confirm the presence of malignant rhabdomyoblasts. For the patient in this report, the detection of metastasis was a daunting moment, leading to the reevaluation of their treatment protocol. Bone marrow metastasis has significant prognostic implications, suggesting a more aggressive tumor biology and necessitating a more intensive therapeutic strategy.
Traditionally, bone marrow involvement in pediatric cancers has been observed more frequently in hematological malignancies. The presence of solid tumor metastasis in the bone marrow often suggests a later-stage disease and often corresponds to poorer outcome measures. This particular case illustrates that clinicians and researchers need to maintain vigilance regarding atypical presentations of RMS, as early detection can significantly influence survivorship outcomes.
One critical aspect of this case is the immediate treatment strategy engaged by the medical team. The patient underwent combination chemotherapy aimed at addressing both the primary tumor and the metastatic spread. The regimen utilized is indicative of current treatment standards, which often incorporate multi-agent chemotherapeutics that target both localized tumors and inhibit further dissemination. The cyclical nature of treatment regimens also plays a crucial role to combat the potential for resistance that may develop during therapy.
The long-term prognosis for patients presenting with bone marrow metastasis from RMS remains a subject of ongoing research. This report posits that despite the advanced stage at diagnosis, factors such as age at treatment initiation, tumor response to chemotherapy, and subsequent surgical interventions can significantly influence survival rates. Pediatric oncology utilizes a plethora of stratification tools to assess these prognostic factors, tailoring treatments to maximize efficacy while minimizing the adverse effects on the patient.
As the authors delve into the complexities of this case, they elucidate the critical need for heightened clinical awareness regarding the heterogeneity of rhabdomyosarcoma presentations. Their study reinforces prior hypotheses about the aggressive behavior of RMS when metastasis to unconventional sites such as the bone marrow occurs. The case draws attention to the importance of early and consistent monitoring for signs of disease progression, a task that requires diligent coordination among healthcare teams.
The study suggests that further research is warranted on the biological underpinnings of rhabdomyosarcoma metastasis. Utilizing emerging technologies such as liquid biopsies may allow researchers to study circulating tumor DNA and identify genetic markers predictive of metastatic behavior. This new frontier in oncology emphasizes the importance of understanding personalized medicine’s role in improving treatment precision and outcomes for young patients.
Moreover, the authors offer insights into future directions for clinical practice and research, emphasizing the urgency for interdisciplinary collaboration among oncologists, surgeons, and researchers dedicated to improving therapies for pediatric cancers. They advocate for improved educational initiatives targeting healthcare professionals about recognizing rare manifestations of common diseases, thus ensuring no child falls through the cracks in their cancer care journey.
In conclusion, the case report of a pediatric patient with rhabdomyosarcoma presenting with bone marrow metastasis underscores a critical aspect of how clinicians must adapt to the complexities of cancer presentations that defy conventional expectations. This detailed analysis not only expands the existing knowledge related to RMS but also draws attention to the pressing need for ongoing research and adaptation of treatment strategies to cater to the nuanced challenges presented by pediatric malignancies.
Such findings serve as a beacon of hope for future innovations in pediatric oncology, laying the groundwork for developing more sophisticated and effective treatment protocols. As we extend our understanding of this complex disease, it becomes increasingly clear that every case offers invaluable lessons that could ultimately enhance therapeutic modalities, ensuring that every child has the best chance for a successful outcome in their fight against cancer.
Subject of Research: Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma with Bone Marrow Metastasis
Article Title: A case report: pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma presenting with bone marrow metastasis
Article References:
Xiong, T., Wan, Q., Yuan, C. et al. A case report: pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma presenting with bone marrow metastasis.
BMC Pediatr 25, 924 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-06310-3
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-06310-3
Keywords: Rhabdomyosarcoma, Pediatric Oncology, Bone Marrow Metastasis, Cancer Treatment, Pediatric Sarcoma, Healthcare Collaboration.