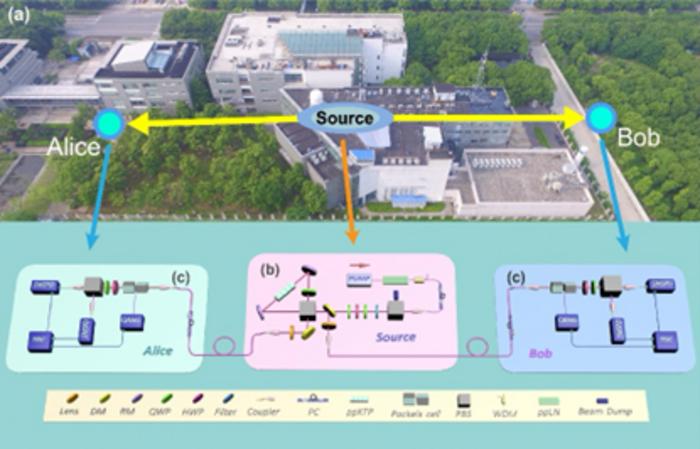
A research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), led by Prof. PAN Jianwei, ZHANG Qiang, and CHEN Kai, in collaboration with CHEN Jingling from Nankai University, has achieved the loophole-free test of Hardy’s paradox for the first time. The team successfully demonstrated Hardy’s nonlocality while closing both the detection efficiency loophole and the locality loophole. Their findings were published in Physical Review Letters as an “Editor’s Suggestion.”

Credit: Si-Ran Zhao et.al
A research team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), led by Prof. PAN Jianwei, ZHANG Qiang, and CHEN Kai, in collaboration with CHEN Jingling from Nankai University, has achieved the loophole-free test of Hardy’s paradox for the first time. The team successfully demonstrated Hardy’s nonlocality while closing both the detection efficiency loophole and the locality loophole. Their findings were published in Physical Review Letters as an “Editor’s Suggestion.”
Hardy’s paradox, introduced by Lucien Hardy in the 1990s, offers a simplified test of local realism—the classical idea that physical properties exist independently of observation and that no signals exceed the speed of light. This paradox exposes the conflict between quantum mechanics and local realism by demonstrating that, under certain conditions where three “Hardy events” have a zero probability, quantum mechanics predicts a non-zero probability for a fourth event, which contradicts local realism.
Experimentally confirming Hardy’s paradox is challenging due to the low probability of the fourth event, requiring high fidelity and efficiency in entanglement sources to distinguish it from noise. Prior experiments faced two main challenges: the locality loophole, where measurement choices could affect outcomes, and the detection efficiency loophole, due to optical losses.
In addressing the locality loophole, the researchers meticulously crafted a space-time experimental setup that ensured the measurement choices were spacelike separated from both the entangled state preparations and the photon detections. This configuration precludes any possibility of the measurement settings being influenced by the outcomes, thereby eliminating the locality loophole.
To tackle the detection efficiency loophole, the study employed a high detection efficiency of 82.2%, which substantially mitigates the impact of optical losses. Moreover, the integration of high-speed quantum random number generators for the selection of measurement settings introduced an element of true randomness, safeguarding against any potential manipulation by local hidden variables. By also incorporating undetected events and double-click events into their analysis through a refined form of Hardy’s inequality, the researchers effectively closed the detection efficiency loophole, presenting a robust experimental framework that stands as a significant contribution to the field of quantum physics.
Finally, the experiment, conducted over six hours, demonstrated a strong violation of Hardy’s paradox, with a significance level of up to 5 standard deviations across 4.32 billion trials. A null hypothesis test confirmed that the probability of explaining the results through local realism is less than 10-16348, providing compelling evidence in favor of quantum nonlocality.
This research deepens our understanding of quantum mechanics and has significant implications for developing quantum technologies such as quantum key distribution and quantum random number certification. It marks an advancement in quantum physics, offering new evidence of quantum nonlocality and paving the way for future quantum information technologies. The referees of the study highly praised the work, noting that “the experimental results, along with the quantified evidence against local realism, are impressive.”
Journal
Physical Review Letters
Article Title
Loophole-Free Test of Local Realism via Hardy’s Violation
Article Publication Date
7-Aug-2024