Exploring the Evolutionary Landscape of Brown Algae: Insights from Genomic Analysis
In the depths of our oceans lies a vast world, teeming with life forms that play pivotal roles in maintaining the ecological balance essential for the well-being of our planet. Among these life forms, brown algae, belonging to the class Phaeophyceae, represent a significant component of marine ecosystems, serving essential functions that range from supporting marine biodiversity to combating climate change. Yet, the intricacies of their evolutionary history have remained relatively uncharted territory until now.
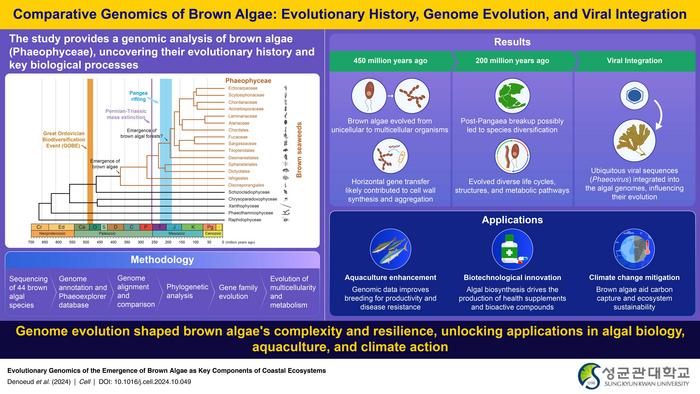
A recent study led by researchers from Sungkyunkwan University has dramatically shifted our understanding of brown algae by unveiling a comprehensive genomic analysis of 44 different species. This groundbreaking research, which was made available online on November 20, 2024, and published on November 27, 2024, in Volume 187, Issue 24 of the esteemed journal Cell, introduces the Phaeoexplorer database. This database stands as a monumental achievement in the field of comparative genomics, offering insights that could significantly advance our comprehension of brown algal evolution and adaptation.
Central to the study’s findings are two major evolutionary milestones fundamental to the history of brown algae. According to lead author Professor Hwan Su Yoon, the transition of brown algae from unicellular organisms to simple multicellular forms occurred approximately 450 million years ago. This transition was catalyzed by horizontal gene transfer from bacteria, which enabled the algal species to create crucial cellular components like alginate and phlorotannin. These evolutionary adaptations provided brown algae with enhanced aggregation capabilities, improved intercellular communication, and a fortified defense mechanism against predators, establishing a cornerstone in their evolutionary saga.
The narrative of brown algal evolution does not stop there. The study highlights a significant diversification event that took place around 200 million years ago, coinciding with the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. Professor Yoon elaborates that this diversification led to the emergence of complex life cycles, notable structural innovations, and specialized metabolic pathways, fundamentally shaping the ecological niches occupied by diverse brown algal species. Furthermore, the genomic analysis revealed an astonishing prevalence of viral sequences integrated within brown algal genomes, with Phaeovirus sequences identified in 67 of the 69 genomes analyzed. This discovery sheds light on a previously overlooked aspect of brown algae’s evolutionary narrative: the influence of viral integration on their genetic evolution and species diversity.
In terms of practical implications, this study paves the way for numerous applications in aquaculture, helping to bolster the selective breeding of commercially important brown algal species such as Undaria pinnatifida and Saccharina japonica. By leveraging this newfound understanding of brown algal genomics, researchers can enhance productivity and disease resistance in aquaculture settings. Moreover, the biosynthetic processes responsible for producing vital compounds like alginate can open avenues for innovations in biotechnology, leading to the development of health supplements, bioactive substances, and eco-friendly biomaterials.
The implications of this study extend significantly into the realm of climate change, highlighting the potential role of brown algae in mitigating environmental degradation. Professor Yoon emphasizes that by analyzing the historical interplay between environmental shifts and brown algal evolution, scientists can gain critical insights into how future climate changes may impact marine biodiversity. The genomic tools established through this research are invaluable for identifying traits that contribute to ecological resilience, which could inform initiatives aimed at developing brown algal strains capable of withstanding climate-induced stresses, including rising temperatures and fluctuating sea levels.
Furthermore, a call for the promotion of kelp forests as “blue carbon” sinks is echoed within this research. Such natural carbon reservoirs are essential for sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, offering a multifaceted solution to combat climate change while simultaneously fostering ecological sustainability in marine ecosystems.
With this pioneering genomic study, the narrative of brown algae gains new depth, enriching our understanding of not only their evolutionary past but also their ecological significance in contemporary marine systems. The findings illuminate the intricate connection between evolution and environmental dynamics, offering a roadmap for harnessing brown algae’s ecological and commercial potential toward promoting a more sustainable future for our oceans and, by extension, our planet.
Through this research, we are reminded of the profound responsibilities we carry toward protecting our oceans—vital ecosystems that harbor biodiversity essential for planetary health. Understanding the evolutionary pathways of organisms like brown algae not only deepens our appreciation for marine life but also empowers us to develop informed strategies that protect and restore these critical ecosystems.
As we navigate the impact of climate change and environmental degradation, the insights achieved through this comprehensive study underscore the importance of integrating scientific knowledge with conservation efforts. By embracing the natural wisdom held within the genetic blueprints of brown algae, we lay the groundwork for a future that acknowledges and nurtures the intricate web of life that sustains us all.
In summary, the genomic exploration of brown algae has not only charted their evolutionary journey but also illuminated their potential to influence marine biodiversity conservation and climate change mitigation. This research stands as a beacon of hope, guiding our understanding of how to leverage the complex interplay between evolution and environmental science for the benefit of our oceans and the larger global ecosystem.
Subject of Research: Brown algae evolutionary genomics
Article Title: Evolutionary genomics of the emergence of brown algae as key components of coastal ecosystems
News Publication Date: November 27, 2024
Web References: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(24)01272-8
References: Hwan Su Yoon et al. (2024).
Image Credits: Professor Hwan Su Yoon, Sungkyunkwan University.
Keywords: brown algae, evolutionary biology, genomics, climate change, biodiversity, aquaculture, biotechnology, ecological sustainability, marine ecosystems, Phaeophyceae.