Huaguang Reef, one of the expansive atolls in the Xisha Islands, is completely mature, stretching 31 kilometers from east to west and 12 kilometers from north to south. Positioned as a concealed reef in the water, only the north and south gates are connected to the sea, attracting frequent fishing activities by local fishermen. However, the ecological environment and biological communities of Huaguang Reef are susceptible to disturbance s from both natural forces and human activities. Consequently, it serves as an exemplary ecosystem for studying typical coral reef fisheries, offering insights into fish species composition and community structure.
Credit: Zhipeng Kang
Huaguang Reef, one of the expansive atolls in the Xisha Islands, is completely mature, stretching 31 kilometers from east to west and 12 kilometers from north to south. Positioned as a concealed reef in the water, only the north and south gates are connected to the sea, attracting frequent fishing activities by local fishermen. However, the ecological environment and biological communities of Huaguang Reef are susceptible to disturbance s from both natural forces and human activities. Consequently, it serves as an exemplary ecosystem for studying typical coral reef fisheries, offering insights into fish species composition and community structure.
This study undertook a survey of coral reef fish resources of Huaguang Reef in 2023. It employed several methods, including hand fishing, diving fishing, underwater video and eDNA detection. Additionally, historical data from 1979 and archival records from the South Sea Institute of Fisheries Research of the Chinese Academy of Fisheries Sciences in 1998, 1999, 2003, and 2005 were integrated.
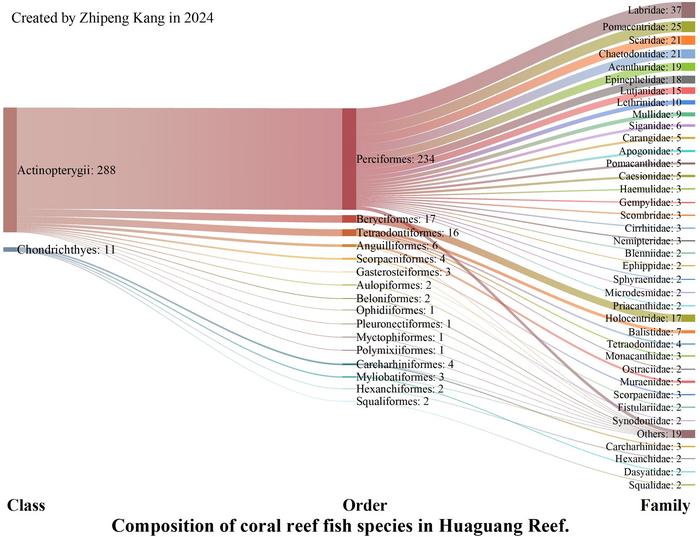
Several notable observations were made. A total of 299 coral reef fish species were identified in Huaguang Reef, categorized into 2 classes, 16 orders, and 56 families, with Perciformes exhibiting the highest species count (234), constituting 78.26% of all species.
In comparison to the period of 1979–2005, there was a reduction in the number of species at the order and family levels in 2023 at Huaguang Reef. Both the average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) and the variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) exhibited a declining trend, indicating disturbances in the fish ecosystem.
Further, the proportion of herbivorous fish at Huaguang Reef remained relatively stable in 2023 compared to the 1979–2005 period. The similarity coefficient of herbivorous fish was the highest among different feeding types, signifying a degraded state of the Huaguang Reef habitat.
In contrast to the 1979–2005 period, a significant decline was observed in large-sized and carnivorous fish species at Huaguang Reef in 2023. The low similarity coefficients for both categories, with undiscovered fish species accounting for 58.49% and 45.76% of their respective taxa in the total list, respectively, suggested a notable impact of overfishing on coral reef fishes. The succession patterns revealed in this study provide a theoretical foundation for advancing the sustainable development of coral reef fish resources in the Xisha Islands and offer valuable insights for the protection and management of coral reef fishes.
The complete findings are published in the KeAi journal Water Biology and Security.
###
Contact the author: Contact author name: Teng Wang, Yong Liu; Affiliation: South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences; Email address: wt3074589@163.com (TW); liuyong@scsfri.ac.cn (YL)
Journal
Water Biology and Security
Method of Research
Survey
Subject of Research
Animals
Discover more from Science
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


