Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical activity raises concerns about its negative impact on children’s healthy brain development and cognitive function.

Credit: Takashi Naito from Graduate School of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical activity raises concerns about its negative impact on children’s healthy brain development and cognitive function.
A recent study published on July 6, 2024, in Volume 14 of Scientific Reports, by doctoral student Takashi Naito from the Graduate School of Sport Sciences, Waseda University, along with Professors Kaori Ishii and Koichiro Oka from the Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University, offers insights into potential solutions. The study investigated the effects of short-duration and light-intensity exercise on increasing cerebral blood flow in children. “Our goal is to develop a light-intensity exercise program that is accessible to everyone, aiming to enhance brain function and reduce children’s sedentary behavior. We hope to promote and implement this program in schools through collaborative efforts,” says Naito.
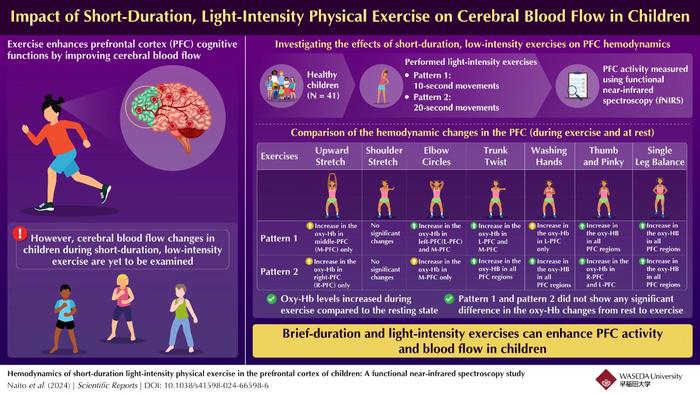
To enhance cognitive performance, it is essential to develop exercise programs that increase cerebral blood flow. While previous studies have established the benefits of moderate-to-vigorous exercise on cognitive functions, changes in cerebral blood flow during light-intensity exercise, particularly in children, is yet to be investigated. To address this gap, the team conducted an experimental study to examine the effects of short-term, light-intensity exercises on prefrontal cortex (PFC) hemodynamics. They focused on exercises that can be easily performed on the spot without special equipment, such as stretching. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), an imaging technique that measures changes in cerebral blood flow through oxy-Hb concentrations, was used for this purpose.
The study enrolled 41 healthy children ranging from fifth-grade elementary to third-year junior high school students. The children were taught seven different types of low-intensity exercises along with associated safety measures. These exercises included Upward Stretch, Shoulder Stretch, Elbow Circles, Trunk Twist, Washing Hands, Thumb and Pinky, and Single-leg Balance. The exercises were performed while seated except Single-leg Balance, with movement patterns lasting for 10 and 20 seconds. Researchers recorded and compared oxy-Hb levels at rest and during exercise.
The study’s results were highly promising, showing a significant increase in oxy-Hb levels in multiple regions of the PFC during all forms of exercise compared to the resting state. However, no significant change in oxy-Hb levels was observed during static stretching with movement in one direction. “By combining the types of exercise that easily increase blood flow in the PFC identified in this study, it is possible to develop an exercise program that everyone can easily engage in to improve children’s executive functions. It may also be used in the future to prevent cognitive decline in adults and the elderly,” explains Naito optimistically.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking study represents a significant step forward in combating sedentary lifestyles and activating brain functions in children, thereby supporting their physical and mental growth. Although this study demonstrated that even short-duration, low-intensity exercise can increase cerebral blood flow in the prefrontal cortex, future research is needed to confirm whether such exercises actually lead to improved cognitive function.
***
Reference
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66598-6
Authors: Takashi Naito1,2, Koichiro Oka3, and Kaori Ishii3
Affiliations
1Graduate School of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
2Organization for the Strategic Coordination of Research and Intellectual Properties, Meiji University
3Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University has produced many changemakers in its history, including nine prime ministers and many leaders in business, science and technology, literature, sports, and film. Waseda has strong collaborations with overseas research institutions and is committed to advancing cutting-edge research and developing leaders who can contribute to the resolution of complex, global social issues. The University has set a target of achieving a zero-carbon campus by 2032, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
To learn more about Waseda University, visit
About Takashi Naito
Takashi Naito is a doctoral student at the Graduate School of Sport Sciences, Waseda University. He holds a Master’s in Sport Sciences from Waseda University with a focus on physical activity, sedentary behavior, cognitive function, and fNIRS. His career includes roles as a part-time lecturer at Surugadai University and a researcher at Meiji University. Naito has received awards for his research and has published extensively on exercise and cognitive health, including studies on light-intensity exercise and its impact on children. He is a member of the Japanese Association of Exercise Epidemiology (JAEE) and the Japanese Society of Health Education and Promotion.
Journal
Scientific Reports
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Hemodynamics of short duration light intensity physical exercise in the prefrontal cortex of children: a functional near infrared spectroscopy study
Article Publication Date
6-Jul-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.