The depletion of energy resources poses a significant threat to the development of human society. Specifically, a considerable amount of low-grade heat (LGH), typically below 100 °C, is currently being wasted. However, if harnessed effectively, it has the potential to significantly improve overall energy utilization efficiency and subsequently reduce carbon dioxide emissions.

Credit: HIGHER EDUCATION PRESS
The depletion of energy resources poses a significant threat to the development of human society. Specifically, a considerable amount of low-grade heat (LGH), typically below 100 °C, is currently being wasted. However, if harnessed effectively, it has the potential to significantly improve overall energy utilization efficiency and subsequently reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
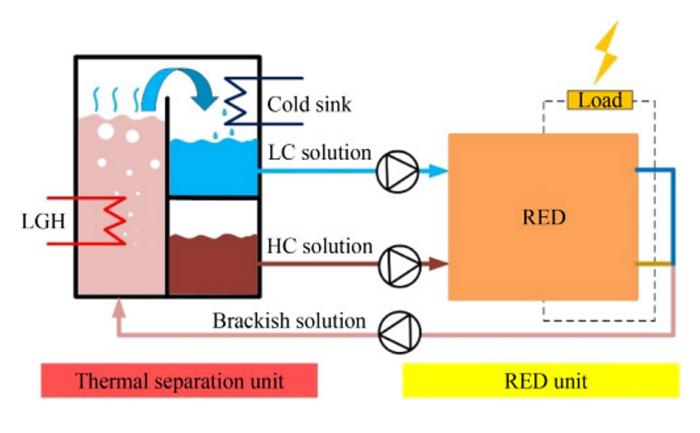
A research group of Junyong Hu from Taiyuan University of Technology has concentrated on developing a new type of reverse electrodialysis heat engine (REDHE). It can efficiently convert LGH into electricity and has emerged as a promising technology in recent years. REDHE incorporates helium-gap diffusion distillation (HGDD) as the thermal separation (TS) unit. The team employed a validated mathematical model to analyze the impact of various operational and structural parameters on the performance of REDHE.
It was found that maintaining a moderate molality of the cold stream, increasing the inlet temperatures of hot and cold streams, lengthening the channels for hot and cold streams, and minimizing the thickness of helium gaps can significantly improve the performance of REDHE. Especially, the REDHE achieved a maximum energy conversion efficiency of 2.96% by reducing the thickness of helium gaps to 3 mm and extending the length of the stream channels to 5 m.
This research is significant as it provides a new technological approach to the effective utilization of low-grade heat energy. The development of the novel REDHE not only helps alleviate energy shortages but also reduces carbon emissions, offering substantial practical application value and environmental benefits for promoting sustainable energy development.
Journal
Frontiers in Energy
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Reverse electrodialysis heat engine with helium-gap diffusion distillation: Energy efficiency analysis
Article Publication Date
30-Apr-2024