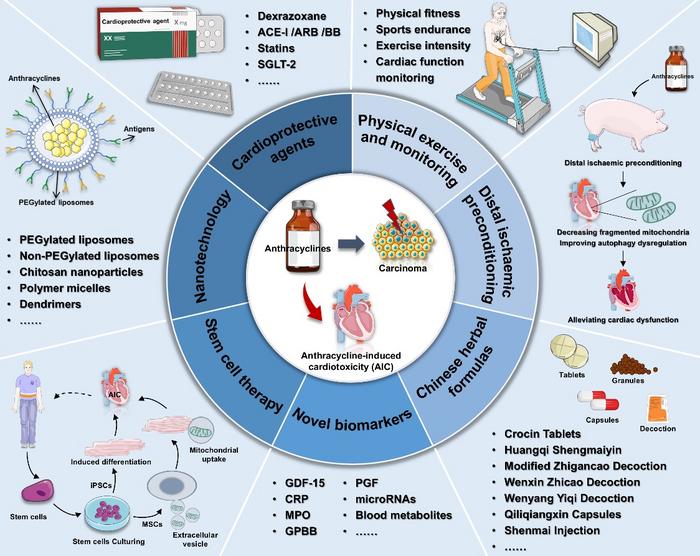
In recent years, our understanding of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC) has evolved significantly, primarily due to advancements in scientific research. This phenomenon, often a side effect of cancer therapies, is among the most critical challenges facing oncologists. AIC occurs when the heart muscle is damaged by anthracycline-based treatments, commonly used in cancer regimens. As cancer survival rates improve, physicians and researchers are increasingly focused on minimizing AIC to enhance patients’ quality of life post-treatment.
Researchers have pinpointed several pathogenic mechanisms that contribute to AIC, which include mitochondrial dysfunction, ferroptosis—a type of cell death characterized by iron accumulation—myocardial senescence, and even genetic and epigenetic alterations. A recent investigation highlighted how disturbances in gut microbiota could also play a role in increasing susceptibility to cardiotoxicity. This complex web of interactions suggests that tailored approaches to treatment may be necessary to protect the heart while effectively treating cancer.
Noteworthy progress is being made in identifying novel biomarkers that can predict the risk of AIC in patients receiving anthracycline therapy. For instance, dysfunctional microRNAs, particularly miRNA-34a, have been linked closely with heart damage in cancer patients. These findings pave the way for more targeted interventions, allowing clinicians to adjust treatment protocols before significant heart damage occurs. Additionally, using human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) offers an innovative platform for modeling AIC, providing insights into patient susceptibility and facilitating the exploration of personalized medicine.
Despite the growing body of knowledge surrounding AIC, traditional treatment strategies remain a cornerstone of cardiovascular safeguarding during cancer therapy. Limiting the cumulative dose of anthracyclines and reformulating drugs, for instance, are common practices that have reduced cardiotoxicity to an extent. Liposomal formulations of doxorubicin present fewer cardiac side effects, but they do not eliminate the risk entirely. The cardioprotective agent dexrazoxane has been utilized to mitigate damage, albeit with limitations regarding its efficacy and application among different patient populations.
Emerging treatment strategies represent a beacon of hope for both researchers and patients. The introduction of nanotechnology in drug delivery is one such advancement, aiming to enhance the precision of drug targeting while minimizing damage to non-cancerous tissues. With nanocarriers, drugs can be delivered directly to affected areas, thus reducing systemic side effects, including cardiotoxicity. This innovative approach could revolutionize how oncologists and cardiologists work together to manage the delicate balance of cancer treatment and cardiac health.
In conjunction with technological advancements, stem cell therapy is garnering attention as an innovative strategy to repair cardiac tissues post-damage. By utilizing the body’s natural regenerative abilities, this therapy shows promise in promoting heart muscle cell regeneration. Researchers are investigating various sources and methods to implement stem cell therapy effectively, with encouraging preliminary results that could reshape future treatment paradigms.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) adds another layer of innovation to the conversation surrounding AIC treatment. The multi-target regulatory capacity of formulas such as Huangqi Shengmaiyin and Qiliqiangxin Capsule exemplifies TCM’s holistic approach. These remedies aim to improve quality of life by addressing cardiovascular symptoms while respecting the body’s overall balance. The integration of TCM principles within Western medical frameworks may offer synergistic benefits for patients dealing with both cancer and its treatment complications.
Another promising concept gaining traction is distal ischemic preconditioning, a technique that induces mild stress to the heart in a controlled manner to protect it from subsequent ischemic damage. This non-pharmacological approach harnesses the body’s intrinsic protective mechanisms and could represent an exciting future direction in AIC management. Further research could elucidate how protocols could be combined with existing cancer therapies to yield improved outcomes.
As we delve deeper into the limitations of current treatment strategies, it becomes evident that a one-size-fits-all approach is inadequate. Cardiotoxicity manifests differently across patient populations, necessitating a more personalized medicine framework. Understanding individual genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors, and health histories will be crucial in shaping future treatment regimens that prioritize both cancer survival and cardiovascular health.
Emerging therapeutic strategies are not without challenges. The integration of new technologies often comes with high costs, raising concerns regarding accessibility and equity in healthcare. Ethical considerations also loom large, particularly as scientists navigate the implications of stem cell usage. Ensuring that the research and treatment avenues pursued are both ethical and safe for patients is of utmost importance, demanding ongoing dialogue among researchers, clinicians, and the communities they serve.
In summary, the landscape of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity is rapidly evolving, driven by a blend of scientific innovation and clinical inquiry. The comprehensive research into underlying mechanisms, alongside the promising advancements in treatment modalities, positions the medical community for a transformative shift in managing AIC. The collaborative efforts among researchers, oncologists, and cardiologists are essential in overcoming present challenges and ensuring that the benefits of cancer treatment do not come at the expense of heart health.
The future holds great promise, but it will require a concerted effort to harmonize the advancements in treatment strategies with the imperative of ensuring patient safety and quality of life in cancer survivors. Sustained investment in research and development will facilitate this transition, ultimately benefiting countless individuals confronting both cancer and the risk of cardiotoxicity.
Subject of Research: Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Article Title: Emerging Strategies in the Management of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity
News Publication Date: Not specified
Web References: Not specified
References: Not specified
Image Credits: ©Science China Press
Keywords: Anthracycline, cardiotoxicity, cancer treatment, nanotechnology, stem cell therapy, Chinese medicine, personalized medicine, ischemic preconditioning.