Social media enthusiasts tend to spice up their text posts with emojis, images, audio, or video to attract more attention. Simple as it is, this technique makes scientific sense: multimodal information is found to be more effective in conveying emotions, as different modalities interact and enhance one another. To advance the understanding of these interactions and improve the analysis of emotions expressed through modality combinations, a Chinese research team introduced a novel two-stage framework using two stacked layers of transformers, state-of-the-art AI models for multimodal sentiment analysis. This study was published May 24 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.

Credit: GUOFENG YI ET AL.
Social media enthusiasts tend to spice up their text posts with emojis, images, audio, or video to attract more attention. Simple as it is, this technique makes scientific sense: multimodal information is found to be more effective in conveying emotions, as different modalities interact and enhance one another. To advance the understanding of these interactions and improve the analysis of emotions expressed through modality combinations, a Chinese research team introduced a novel two-stage framework using two stacked layers of transformers, state-of-the-art AI models for multimodal sentiment analysis. This study was published May 24 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Current research in multimodal sentiment analysis often focuses on either fusing different modalities or addressing intricate interactions or adaptations between different types of fused information. Either approach alone can lead to information loss. This team’s framework, on the other hand, fuses information in two stages to effectively capture information on both levels. It was tested on three open datasets—MOSI, MOSEI, and SIMS—and performed better than or as well as the benchmark models.
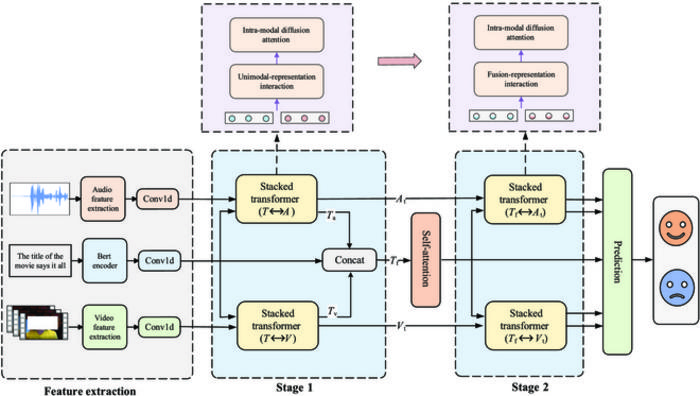
The general workflow of this framework includes feature extraction, two stages of information fusion, and emotion prediction. First, text, audio, and video signals taken from source video clips are processed through their corresponding feature extractors and then encoded with additional context information into context-aware representations. Next, the three types of representations fuse for the first time: the text representations interact with the audio and video representations, allowing each modality to adapt to the others during the process, and the results further integrate with the original text representations. The text-centered output from the first stage then fuses with the adapted non-text representations so that they can enhance each other before the final, enriched output is ready for the emotion prediction stage.
The core of the team’s framework is stacked transformers and consists of bidirectional cross-modal transformers and a transformer encoder. These components correspond to two functional layers: the bidirectional interaction layer allows cross-modal interaction and is where the first-stage fusion occurs, and the refine layer addresses the more nuanced second-stage fusion.
To enhance the performance of the framework, the team implemented an attention weight accumulation mechanism that aggregates the attention weights of the text and non-text modalities during fusion to extract deeper shared information. Attention, a key concept in transformers, enables the model to identify and focus on the most relevant parts of the data. The team’s stacked transformers adopt two types of attention mechanism: the bidirectional cross-modal transformers use cross-attention, and the transformer encoder uses self-attention.
The future work of the team will focus on integrating more advanced transformers to improve computational efficiency and mitigate the inherent challenges associated with the self-attention mechanism.
Journal
Intelligent Computing
Article Title
A Two-Stage Stacked Transformer Framework for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Article Publication Date
24-May-2024