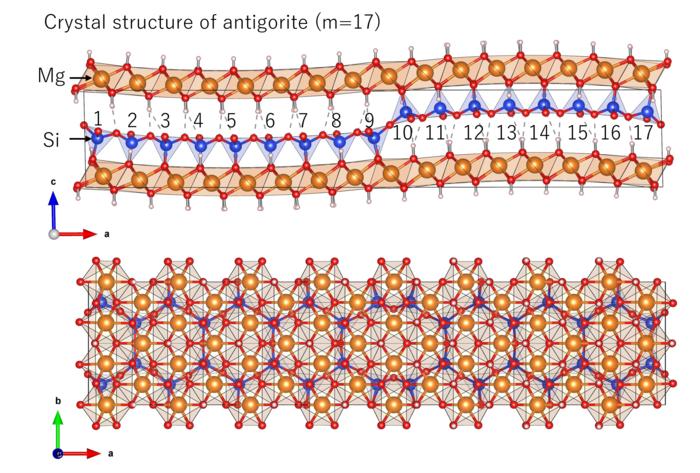
Antigorite is a type of serpentine, which is the most abundant hydrated mineral on the Earth. It is widely believed that this mineral is the main carrier of water deep into the Earth in subducting oceanic plates. It has a wavy structure along the a-axis, and in nature, several polysomes with different m-values (m=13-24) have been identified (polysomatism). The m-value is defined as the number of tetrahedra contained in one wavelength, and is controlled by the difference in length between the octahedral layer and the tetrahedral layer (Figure1). This length is mainly determined by the size of the MgO6 octahedra and SiO4 tetrahedra, and is therefore expected to vary as a function of pressure and temperature. However, it is not well understood how the m-value of antigorite changes under the high pressure and temperature conditions in the Earth.
Credit: Jun Tsuchiya, Ehime University
Antigorite is a type of serpentine, which is the most abundant hydrated mineral on the Earth. It is widely believed that this mineral is the main carrier of water deep into the Earth in subducting oceanic plates. It has a wavy structure along the a-axis, and in nature, several polysomes with different m-values (m=13-24) have been identified (polysomatism). The m-value is defined as the number of tetrahedra contained in one wavelength, and is controlled by the difference in length between the octahedral layer and the tetrahedral layer (Figure1). This length is mainly determined by the size of the MgO6 octahedra and SiO4 tetrahedra, and is therefore expected to vary as a function of pressure and temperature. However, it is not well understood how the m-value of antigorite changes under the high pressure and temperature conditions in the Earth.
In this study, we used the first-principles method to calculate the free energy (enthalpy) of antigorites with different m-values (m=14-19) under pressure, and compared the stability of antigorites with different m-values. As a result, it was found that the m-value of the most stable antigorite gradually decreases. In other words, antigorite gradually dehydrates as pressure increases, changing into a structure with a shorter wavelength.
This suggests that the structure of antigorite in the oceanic lithosphere may gradually evolve into a polysome with a smaller m-value that differs from the antigorite observed under ambient pressure or near-surface pressure conditions (i.e. m=17) (Figure2). Such changes in m-values are accompanied by minor dehydration reactions. Changes in the amount of water in rocks and minerals due to the polysomatism of antigorite in subduction zones may affect the distribution of intermediate-depth earthquakes, such as those observed in the double seismic zone.
Journal
Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth
Discover more from Science
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


