China’s energy landscape is at a pivotal juncture, driven by an urgent need for decarbonization in response to climate change. As the world’s largest carbon emitter, China has recognized the critical importance of transforming its energy sector to achieve carbon neutrality. In a recent study published in Technology Review for Carbon Neutrality, a research team affiliated with Tsinghua University underscored the complexities and challenges of deploying advanced technologies that are crucial for this transformation. Their findings illuminate the way forward, showcasing a multifaceted approach to meeting both technological and policy needs.
The research highlights that China’s energy sector faces a dual challenge: reducing greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining energy security and economic growth. Consciously balancing these priorities is not a straightforward task, and it necessitates the development of a comprehensive roadmap. This roadmap would lay out strategic directions and provide actionable insights into the technological advancements needed for decarbonization. The team’s analysis integrates both supply and demand perspectives, emphasizing the necessity of addressing near-term and long-term goals simultaneously.
A significant part of the study involves evaluating the obstacles hindering China’s path to carbon neutrality. Key issues range from the geographical mismatch between energy production and consumption to the challenge of integrating emerging energy systems with existing fossil fuel infrastructure. This understanding is particularly crucial given that China’s energy consumption patterns are not uniformly distributed across the country. The research brings to light that policymakers must consider regional disparities and infrastructure deficits when designing a decarbonization strategy.
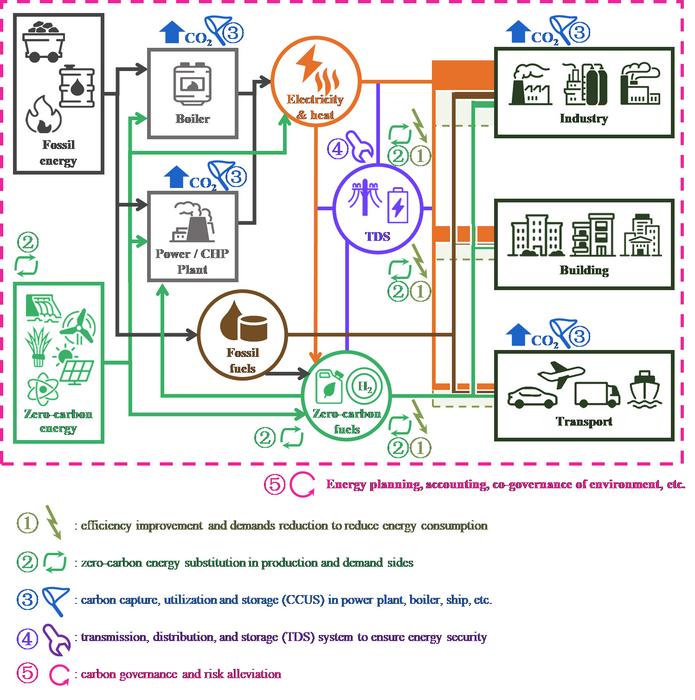
Three principal pathways for emissions reduction have been identified. Firstly, enhancing energy efficiency by optimizing existing systems can lead to considerable reductions in energy demand. Secondly, transitioning towards zero-carbon energy sources will require a massive shift in how energy is produced and consumed. This transition includes embracing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, as well as nuclear power, harnessing technologies that do not emit greenhouse gases. Finally, the adoption of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies presents a potential avenue for mitigating emissions from sectors that are harder to decarbonize.
The complexity of implementing these technologies cannot be understated. For instance, as China increases its reliance on variable renewable energy sources, the stability of its power grid may be jeopardized. The research outlines that to mitigate this risk, enabling technologies such as improved grid transmission and distribution systems, along with robust energy storage solutions, are essential. Additionally, managing carbon emissions will require an organized governance system that ensures transparency, accountability, and effective risk management.
As China navigates this transformative landscape, the study emphasizes that successful decarbonization depends on continuous innovation in energy technologies. The need for a top-level design of a technology roadmap cannot be emphasized enough; it would provide a structured approach to the dynamic and fast-evolving nature of energy technology development. This roadmap should be revisited regularly, allowing for adjustments and improvements as new technologies and methods emerge, thereby ensuring China’s competitiveness on the global stage.
Moreover, the collaborative efforts of multidisciplinary teams—featuring experts from various institutions, including Tsinghua University and the Administrative Centre for China’s Agenda 21—are essential. These collaborations create a rich dialogue that encourages knowledge sharing and synthesis of ideas, resulting in a collective understanding of the technological, economic, and regulatory challenges at hand. The pursuit of a sustainable energy future will necessitate the amalgamation of insights from multiple fields, underscoring the interconnectedness of energy, environment, and policy.
The research team’s efforts have also been supported by significant funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST. Such backing exemplifies the importance that these organizations place on research and development in the pursuit of carbon neutrality. It reflects a growing awareness of the need for strategic investment in technology to help bridge the gap between ambitious emissions reduction goals and the realization of those targets.
With the publication of their work, the team hopes to contribute toward a more informed discourse on the pathways to decarbonization. Their findings aim to serve as a resource for policymakers, businesses, and researchers alike, guiding strategic decisions that will ultimately shape the future of China’s energy sector. As the global clock ticks toward mounting climate deadlines, the urgency for action in this domain cannot be overstated. Collaborative, evidence-based approaches rooted in sound technology and policy frameworks are essential for ensuring a successful transition to a carbon-neutral economy.
In a world increasingly characterized by climate extremes and environmental disruptions, the implications of China’s decarbonization efforts extend beyond national borders. As a key player in international climate dynamics, how China progresses toward its carbon neutrality goals will influence global climate strategies. Its roadmap for innovation could provide a model for other nations grappling with the same challenges, potentially fostering a global coalition for emissions reduction.
The journey to a decarbonized energy sector is fraught with challenges, yet it is also ripe with opportunities for innovation and development. That said, constant evaluation and readiness to adapt to new realities must become part of the foundational strategy moving forward. By prioritizing an integrative approach and harnessing the full potential of technological advancements, China may pave the way for a sustainable energy future, serving as both a leader and a case study for other nations in their quest for carbon neutrality.
The breadth of insights provided in this research serves as a clarion call for all stakeholders engaged in the development of technologies aimed at addressing climate change challenges. Ultimately, the paper represents a critical step in fostering a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between technology, energy policy, and greenhouse gas emissions reduction strategies. As the energy transition gathers momentum worldwide, attention to these findings will be essential for creating resilient, innovative, and sustainable energy systems.
Subject of Research: Energy sector decarbonization in China
Article Title: Energy sector decarbonization in China: macro challenges, supporting technologies and systems, and policy recommendations
News Publication Date: 31-Dec-2024
Web References: DOI
References: Technology Review for Carbon Neutrality
Image Credits: Technology Review for Carbon Neutrality, Tsinghua University Press
Keywords: China, energy sector, decarbonization, carbon neutrality, technology, renewable energy, CCUS, policy recommendations