A research team led by Director KIM Eunjoon of the Center for Synaptic Brain Dysfunctions and Director KIM Seong-Gi of the Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) has identified the primary cause of sensory hypersensitivity related to autism spectrum disorders (ASD).

Credit: Institute for Basic Science
A research team led by Director KIM Eunjoon of the Center for Synaptic Brain Dysfunctions and Director KIM Seong-Gi of the Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) has identified the primary cause of sensory hypersensitivity related to autism spectrum disorders (ASD).
Autism affects approximately 1 in 36 individuals and is marked by significant challenges in social interaction and communication. Around 90% of autism patients also suffer from abnormal sensory hypersensitivity that deeply affects their daily functioning. This hypersensitivity results in exaggerated or dampened responses to common sensory stimuli such as sound, light, and touch, which leads to considerable stress and further social withdrawal. The precise brain region responsible for this sensory dysfunction is unknown, which hinders treatment efforts.
The IBS researchers studied an ASD mouse model with a mutation in the Grin2b gene, which encodes the GluN2B subunit of NMDA receptors. NMDA receptors, a type of glutamate receptor in the brain, have garnered attention in the context of autism due to their crucial role in synaptic transmission and neural plasticity. It was hypothesized that the Grin2b gene mutation in mice would induce ASD-like phenotypes, including sensory abnormalities, and that certain brain mechanisms may play important roles.
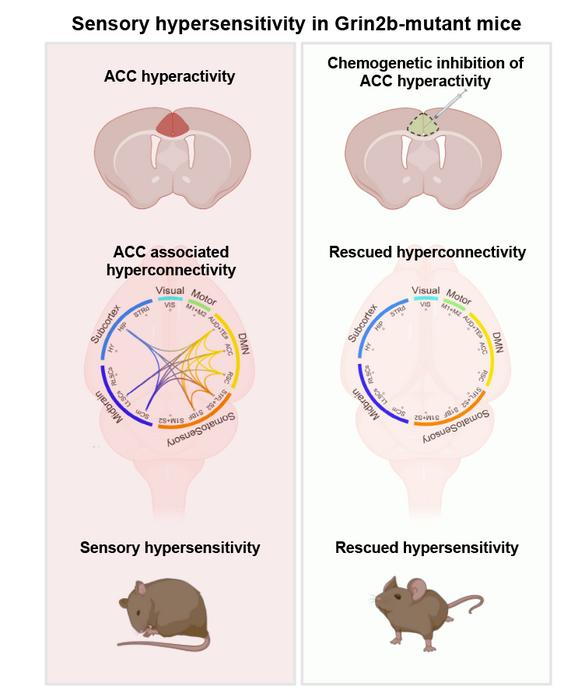
The researchers monitored neural activity and functional connectivity in the brains of these mice using activity-dependent markers and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In these mice, the researchers discovered increased neuronal activity in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). The ACC is one of the higher-order cortical regions that have been extensively studied for cognitive and emotional brain functions, but have been understudied for brain disease-related sensory abnormalities.
Interestingly, when the hyperactivity of ACC neurons was inhibited using chemogenetic methods, sensory hypersensitivity were normalized, indicating the pivotal role of ACC hyperactivity in sensory hypersensitivity associated with autism.
Director KIM Eunjoon states, “This new research demonstrates the involvement of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), which has been known for its deep association with cognitive and social functions, in sensory hypersensitivity in autism.”
The hyperactivity of the ACC was also associated with the enhanced functional connectivity between the ACC and other brain areas. It is believed both hyperactivity and the hyperconnectivity of the ACC with various other brain regions are involved with sensory hypersensitivity in Grin2b-mutant mice.
Director KIM Seong-Gi states, “Past studies attributed peripheral neurons or primary cortical areas to be important for ASD-related sensory hypersensitivity. These studies often only focused on the activity of a single brain region. In contrast, our study investigates not only the activity of ACC but also the brain-wide hyperconnectivity between the ACC and various cortical/subcortical brain regions, which gives us a more complete picture of the brain.”
The researchers plan to study the detailed mechanisms underlying the increased excitatory synaptic activity and neuronal hyperconnectivity. They suspect that the lack of Grin2b expression may inhibit the normal process of weakening and pruning synapses that are less active so that relatively more active synapses can participate in refining neural circuits in an activity-dependent manner. Other areas of research interest is studying the role of ACC in other mouse models of ASD.
This study was published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Journal
Molecular Psychiatry
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Anterior cingulate cortex-related functional hyperconnectivity underlies sensory hypersensitivity in Grin2b-mutant mice
Article Publication Date
4-May-2024