Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center have isolated human monoclonal antibodies against influenza B, a significant public health threat that disproportionately affects children, the elderly and other immunocompromised individuals.

Credit: Illustration by Elad Binshtein, PhD, and Anthony Czelusniak
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center have isolated human monoclonal antibodies against influenza B, a significant public health threat that disproportionately affects children, the elderly and other immunocompromised individuals.
Seasonal flu vaccines cover influenza B and the more common influenza A but do not stimulate the broadest possible range of immune responses against both viruses. In addition, people whose immune systems have been weakened by age or illness may not respond effectively to the flu shot.
Small-molecule drugs that block neuraminidase, a major surface glycoprotein of the influenza virus, can help treat early infection, but they provide limited benefit when the infection is more severe, and they are generally less effective in treating influenza B infections. Thus, another way to combat this virus is needed.
Reporting in the journal Immunity, the VUMC researchers describe how, from the bone marrow of an individual previously vaccinated against influenza, they isolated two groups of monoclonal antibodies that bound to distinct parts of the neuraminidase glycoprotein on the surface of influenza B.
One of the antibodies, FluB-400, broadly inhibited virus replication in laboratory cultures of human respiratory epithelial cells. It also protected against influenza B in animal models when given by injection or through the nostrils.
Intranasal antibody administration may be more effective and have fewer systemic side effects than more typical routes — intravenous infusion or intramuscular injection — in part because intranasal antibodies may “trap” the virus in the nasal mucus, thereby preventing infection of the underlying epithelial surface, the researchers suggested.
These findings support the development of FluB-400 for the prevention and treatment of influenza B and will help guide efforts to develop a universal influenza vaccine, they said.
“Antibodies increasingly have become an interesting medical tool to prevent or treat viral infections,” said the paper’s corresponding author, James Crowe Jr., MD. “We set out to find antibodies for the type B influenza virus, which continues to be a medical problem, and we were happy to find such especially powerful molecules in our search.”
Crowe, who holds the Ann Scott Carell Chair, is University Distinguished Professor of Pediatrics and director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Center, which has isolated monoclonal antibodies against a host of viral infections, including COVID-19.
The paper’s first author, Rachael Wolters, DVM, PhD, is a former graduate student in the Crowe lab. Other VUMC co-authors are Elaine Chen, PhD, Ty Sornberger, Luke Myers, Laura Handal, Taylor Engdahl, Nurgen Kose, Lauren Williamson, PhD, Buddy Creech, MD, and Katherine Gibson-Corley, DVM, PhD.
This study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants T32AI112541, K01OD036063 and U01AI150739, NIH-HHS contracts 75N93019C00074 and 75N93019C00073, and the Collaborative Influenza Vaccine Innovation Centers program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
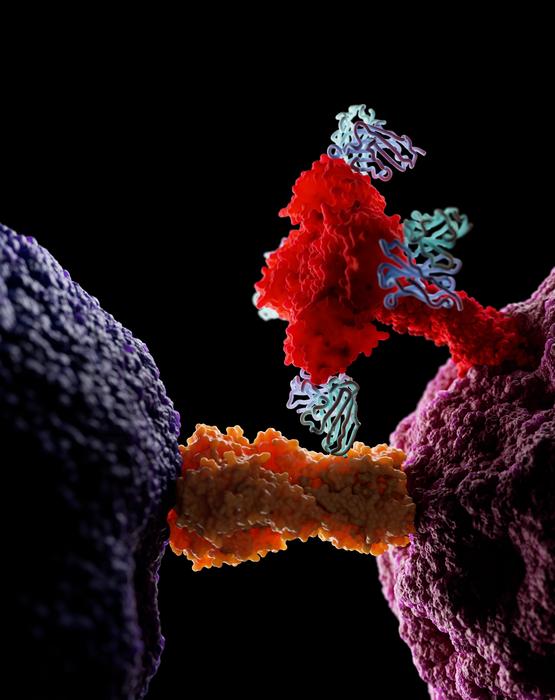
Illustration: A 3D rendering shows one of the isolated antibodies, FluB-393, (blue) binding to the neuraminidase surface glycoprotein (red) of the influenza type B virus to prevent infection.
(illustration by Elad Binshtein, PhD, and Anthony Czelusniak)
Journal
Immunity
Article Title
Article|Online Now PDF Figures Save Share Reprints Request Isolation of human antibodies against influenza B neuraminidase and mechanisms of protection at the airway interface
Article Publication Date
31-May-2024