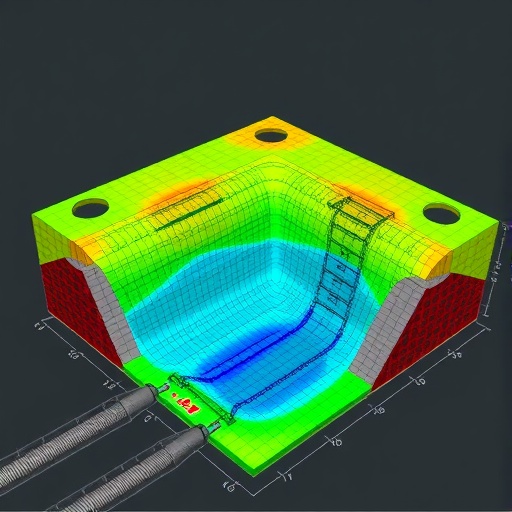
In the constantly evolving landscape of geotechnical engineering, the effective management and mitigation of ground vibrations are paramount, especially in urban environments where infrastructure development is often confined to tightly packed spaces. In this regard, researchers Hu, Chen, and Xu have made significant strides in understanding how open trenches, augmented with horizontal hollow pipes, can serve as an effective solution for vibration mitigation. Their study, titled “3D dynamic numerical modeling on vibration mitigation efficiency of open trench with horizontal hollow pipes,” published in Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, lays the groundwork for future innovations in noise and vibration control.
Vibration mitigation is crucial in various construction projects, especially those near sensitive structures. Excessive vibrations can cause damage to buildings, compromise their structural integrity, and adversely affect residents’ comfort. Traditional methods to dampen vibrations include using massive barriers or isolation pads, yet these solutions often come with limitations related to cost, space, and effectiveness. The authors present a novel approach that leverages the principles of dynamics and fluid mechanics to enhance the passive vibration attenuation properties of trench systems.
The researchers employ a comprehensive 3D dynamic numerical modeling technique that simulates real-world conditions. By integrating complex interactions between the soil, trench, and surrounding infrastructure, the study provides new insights into how horizontal hollow pipes can influence the propagation of vibrational waves through geological layers. This approach goes beyond theoretical assumptions, allowing practitioners to predict the effectiveness of vibration mitigation strategies accurately.
One of the standout features of this research is its focus on the open trench’s geometry and configuration. Unlike conventional solid barriers, which can reflect vibrations, open trenches act as energy sinks. By absorbing vibrational energy through their shape and structure, they prevent harmful vibrations from reaching adjacent buildings. The inclusion of horizontal hollow pipes further amplifies this effect by introducing additional damping characteristics, which the model analyzes in detail. The results indicate a significant reduction in vibration intensity when these innovative elements are included.
Moreover, the research delves into the material properties of the soils surrounding the trench. Understanding the soil-structure interaction is essential for effective vibration mitigation. Differing soil types exhibit varied responses to applied forces, and this variability can greatly influence the effectiveness of the proposed trench system. The numerical model accounts for these differences, creating a robust framework for assessing the viability of using open trenches in diverse geological settings.
A critical aspect of this study is its application potential. As cities grow and infrastructure needs expand, the demand for effective vibration mitigation solutions is increasing. Conventional methods often fall short, necessitating innovative approaches that can be integrated seamlessly into existing urban layouts. By utilizing open trenches with horizontal hollow pipes, engineers could provide an effective solution that mitigates the adverse effects of ground vibrations without requiring extensive alterations to current infrastructure.
Furthermore, the implications of this research extend beyond urban environments. Various sectors, including transportation and energy, stand to benefit from advancements in vibration mitigation strategies. Railways, for example, are notorious for producing excessive vibrations that can affect nearby communities. By implementing the trench and pipe system, significant reductions in vibration levels could enhance the quality of life for residents living near rail lines.
The researchers acknowledge that while their findings are promising, further empirical validation is necessary. Field tests would foray into the practical application of the model’s predictions, offering real-world data to complement the numerical findings. This next step is vital for transitioning from theoretical insights to tangible solutions that urban planners and engineers can deploy.
In addition to academic implications, this study taps into environmental concerns relating to construction practices. By prioritizing vibration mitigation, structures can be built with minimal disruption to surrounding communities and ecosystems. This consideration aligns with the broader goals of sustainable engineering, where innovative strategies are developed not only to improve functionality but also to enhance societal acceptance of construction projects.
Finally, as the field of vibration mitigation continues to evolve, ongoing research and development will play pivotal roles. The integration of advanced materials, novel designs, and cutting-edge computational methods is critical to improving the reliability and efficiency of these systems. As cities continue to expand vertically and horizontally, the necessity for effective vibration control mechanisms remains clear. This research by Hu, Chen, and Xu is a significant step towards achieving that goal, providing a foundation that future studies can build upon to refine vibration mitigation technologies further.
The journey towards effective vibration control is just beginning. As we embrace innovative techniques such as the ones presented in this study, we can look forward to enhanced urban living conditions and safer infrastructure, ensuring that growth and development do not come at the expense of community well-being.
Subject of Research: Vibration mitigation in urban environments through innovative trench systems.
Article Title: 3D dynamic numerical modeling on vibration mitigation efficiency of open trench with horizontal hollow pipes.
Article References: Hu, Z., Chen, Q., Xu, C. et al. 3D dynamic numerical modeling on vibration mitigation efficiency of open trench with horizontal hollow pipes. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 24, 795–809 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-025-2337-1
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: July 2025
Keywords: Vibration mitigation, open trench, horizontal hollow pipes, urban engineering, soil-structure interaction, dynamic modeling, infrastructure development, sustainable engineering.