A Research team led by academician GUO Guangcan, Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. LIU Biheng from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. Giulio Chiribella from the University of Hong Kong, constructed a coherent superposition of quantum evolution with two opposite directions in a photonic system and confirmed its advantage in characterizing input-output indefiniteness. Their study was published in Physical Review Letters.

Credit: Image by Prof. LI Chuanfeng’s team
A Research team led by academician GUO Guangcan, Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. LIU Biheng from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. Giulio Chiribella from the University of Hong Kong, constructed a coherent superposition of quantum evolution with two opposite directions in a photonic system and confirmed its advantage in characterizing input-output indefiniteness. Their study was published in Physical Review Letters.
The notion that time flows inexorably from the past to the future is deeply rooted in people’s mind. However, the laws of physics that govern the motion of objects in the microscopic world do not deliberately distinguish the direction of time. To be more specific, the basic equations of motion of both classical and quantum mechanics are reversible, and changing the direction of the time coordinate system of a dynamical process (possibly along with the direction of some other parameters) still constitutes a valid evolution process. This is known as time reversal symmetry. In quantum information science, time reversal has attracted great interest due to its applications in multitime quantum states, simulations of closed timelike curves, and inversion of unknown quantum evolutions. However, time reversal is difficult to realize experimentally.
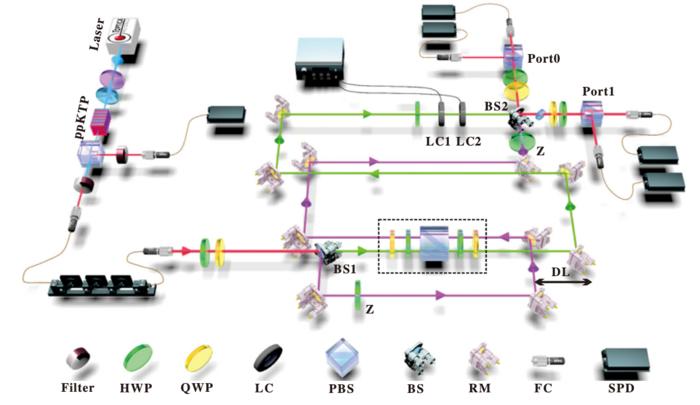
To tackle this problem, the team constructed a class of quantum evolution processes in a photonic setup by extending the time reversal to the input-output inversion of quantum device. When exchanging the input and output ports of a quantum device, the resulting evolution satisfied the time-reversal properties of the initial evolution, thus obtaining a time-reversal simulator for quantum evolution. On this basis, the team further quantized the evolution time direction, achieving the coherent superposition of the quantum evolution and its inverse evolution. They also characterized the structures using quantum witness techniques.
Compared to the scenario of a definite evolution time direction, the quantization of the time direction showed significant advantages in quantum channel identification. In this study, researchers used the device to distinguish between two sets of quantum channels with a 99.6% success probability, while the maximum success probability of a definite time direction strategy was only 89% with the same resource consumption.
The study revealed the potential of input-output indefiniteness as a valuable resource for advancements in quantum information and photonic quantum technologies.
Journal
Physical Review Letters
Article Title
Experimental Demonstration of Input-Output Indefiniteness in a Single Quantum Device
Article Publication Date
16-Apr-2024