Strawberries, treasured for their flavor and health benefits, have been at the forefront of breeding programs targeting enhanced sensory and nutritional profiles. Despite advances, the intricate genetic makeup of these fruits has complicated efforts to improve them. This new study offers a breakthrough by identifying key genetic markers and candidate genes that control quality traits, enabling more precise and successful breeding strategies to cultivate strawberries that are juicier, more vibrant, and longer-lasting.
Strawberry breeding faces the challenge of balancing genetic diversity with the improvement of fruit quality traits like firmness and flavor. Traditional breeding methods have often struggled to meet these dual demands. Recent advancements in genetic research, particularly genome-wide association studies (GWAS), have provided new opportunities to explore and enhance these traits. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need to conduct in-depth research on the genetic factors that influence fruit quality in strawberries, leveraging the rich genetic diversity available in European strawberry varieties.
Researchers from the University of Bordeaux, in collaboration with Invenio, have made significant strides in strawberry research. Their findings (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae137), published in the journal Horticulture Research on May 14, 2024, explore the genetic evolution of strawberry diversity and identify molecular markers for breeding programs, aiming to enhance the fruit’s weight, firmness, composition, and appearance.
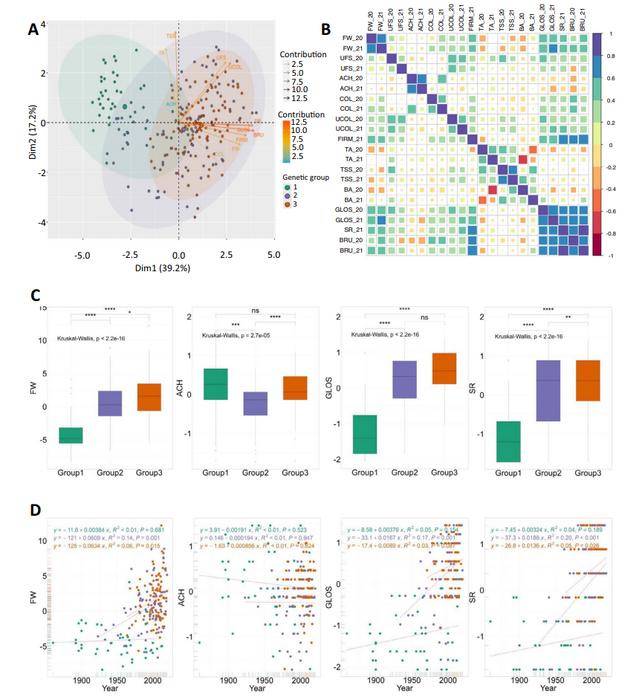
The study uncovered significant genetic markers linked to key fruit quality traits, such as fruit weight, firmness, and glossiness. Utilizing GWAS, the researchers identified 71 associations with 11 different quality traits, validating known markers and discovering new quantitative trait loci (QTL). Notably, three of the six selective sweeps identified are associated with glossiness and skin resistance—traits that enhance fruit appeal and shelf life. These findings demonstrate substantial improvements in breeding targets achieved across European and American cultivars. The study also highlighted regions of reduced genetic diversity due to selection pressure, underscoring the impact of breeding on genetic variation. This research emphasizes the value of untapped genetic resources in European strawberries, offering promising avenues for breeding programs to enhance fruit quality without compromising flavor and color.
Dr. Béatrice Denoyes, one of the lead researchers, stated, “This study offers a comprehensive view of strawberry genetic diversity and its impact on fruit quality. The identification of new genetic markers will significantly aid breeding programs focused on improving fruit traits that are important to both growers and consumers.”
The findings from this study have substantial implications for strawberry breeding programs. By utilizing the newly identified genetic markers, breeders can more effectively select traits that enhance fruit quality, such as firmness and glossiness. This will not only improve the consumer experience but also reduce postharvest losses, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.

Credit: Horticulture Research
Strawberries, treasured for their flavor and health benefits, have been at the forefront of breeding programs targeting enhanced sensory and nutritional profiles. Despite advances, the intricate genetic makeup of these fruits has complicated efforts to improve them. This new study offers a breakthrough by identifying key genetic markers and candidate genes that control quality traits, enabling more precise and successful breeding strategies to cultivate strawberries that are juicier, more vibrant, and longer-lasting.
Strawberry breeding faces the challenge of balancing genetic diversity with the improvement of fruit quality traits like firmness and flavor. Traditional breeding methods have often struggled to meet these dual demands. Recent advancements in genetic research, particularly genome-wide association studies (GWAS), have provided new opportunities to explore and enhance these traits. Based on these challenges, there is a pressing need to conduct in-depth research on the genetic factors that influence fruit quality in strawberries, leveraging the rich genetic diversity available in European strawberry varieties.
Researchers from the University of Bordeaux, in collaboration with Invenio, have made significant strides in strawberry research. Their findings (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae137), published in the journal Horticulture Research on May 14, 2024, explore the genetic evolution of strawberry diversity and identify molecular markers for breeding programs, aiming to enhance the fruit’s weight, firmness, composition, and appearance.
The study uncovered significant genetic markers linked to key fruit quality traits, such as fruit weight, firmness, and glossiness. Utilizing GWAS, the researchers identified 71 associations with 11 different quality traits, validating known markers and discovering new quantitative trait loci (QTL). Notably, three of the six selective sweeps identified are associated with glossiness and skin resistance—traits that enhance fruit appeal and shelf life. These findings demonstrate substantial improvements in breeding targets achieved across European and American cultivars. The study also highlighted regions of reduced genetic diversity due to selection pressure, underscoring the impact of breeding on genetic variation. This research emphasizes the value of untapped genetic resources in European strawberries, offering promising avenues for breeding programs to enhance fruit quality without compromising flavor and color.
Dr. Béatrice Denoyes, one of the lead researchers, stated, “This study offers a comprehensive view of strawberry genetic diversity and its impact on fruit quality. The identification of new genetic markers will significantly aid breeding programs focused on improving fruit traits that are important to both growers and consumers.”
The findings from this study have substantial implications for strawberry breeding programs. By utilizing the newly identified genetic markers, breeders can more effectively select traits that enhance fruit quality, such as firmness and glossiness. This will not only improve the consumer experience but also reduce postharvest losses, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
Funding information
The project was funded by the Nouvelle-Aquitaine Region and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) (REGINA project no. 67822110; AgirClim project No. 2018-1R20202); and European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (BreedingValue project No. 101000747; PRIMA-Partnership 2019–22 Med-Berry project).
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2023. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
Journal
Horticulture Research
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Exploration of a European-centered strawberry diversity panel provides markers and candidate genes for the control of fruit quality traits
Article Publication Date
14-May-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.