The liver’s ability to communicate with other organs is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, particularly through signaling pathways. During liver regeneration, communication with organs such as the brain, pancreas, intestine, and heart is vital, mediated by chemical messengers like hormones, cytokines, and growth factors. Among these signals, the TGF-β and HIPPO pathways are critical, functioning as tumor suppressors and regulating liver development and regeneration. The review focuses on these pathways’ interplay in maintaining liver homeostasis, facilitating regeneration, and contributing to diseases like hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and cancer.

Credit: Marina Macías-Silva, Victor M. Color-Aparicio
The liver’s ability to communicate with other organs is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, particularly through signaling pathways. During liver regeneration, communication with organs such as the brain, pancreas, intestine, and heart is vital, mediated by chemical messengers like hormones, cytokines, and growth factors. Among these signals, the TGF-β and HIPPO pathways are critical, functioning as tumor suppressors and regulating liver development and regeneration. The review focuses on these pathways’ interplay in maintaining liver homeostasis, facilitating regeneration, and contributing to diseases like hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and cancer.
Liver Physiology and Hepatic Contexts in Health and Disease
The liver performs multiple crucial functions, including nutrient metabolism, bile production for fat digestion, blood detoxification, plasma protein synthesis, blood clotting regulation, and immune response. These functions are regulated by the interplay of various signaling pathways. The TGF-β and HIPPO pathways are particularly relevant due to their roles in tumor suppression and liver regulation. This review delves into the specific interactions between these pathways and their impact on liver physiology and pathology.
TGF-β and HIPPO Signaling Pathways
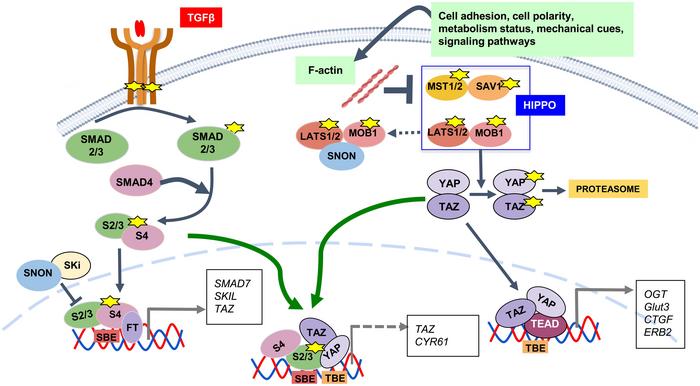
The TGF-β pathway is essential for regulating cell growth, differentiation, and immune responses. It functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. The HIPPO pathway controls organ size by regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis, acting through its core components MST1/2, LATS1/2, and downstream effectors YAP and TAZ. In the liver, these pathways interact through various molecular mechanisms, contributing to the regulation of liver development, size, and regeneration.
- TGF-β Pathway: TGF-β is a cytokine that plays a critical role in regulating cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. In the liver, TGF-β signaling is involved in maintaining liver homeostasis and responding to injury by modulating inflammation and fibrosis.
- HIPPO Pathway: The HIPPO pathway is a kinase cascade that regulates organ size by controlling cell proliferation and apoptosis. It comprises several core components, including MST1/2 (mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 1/2) and LATS1/2 (large tumor suppressor kinase 1/2), which ultimately regulate the activity of the transcription coactivators YAP (Yes-associated protein) and TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif).
Interplay of TGF-β and HIPPO Pathways in Liver Regeneration
In liver regeneration, the TGF-β and HIPPO pathways exhibit significant crosstalk. The TGF-β pathway can inhibit YAP/TAZ activity, crucial components of the HIPPO pathway, thus modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. This interaction is vital for restoring liver function after injury. The pathways’ interplay ensures a balanced regenerative response, preventing excessive cell proliferation that could lead to tumorigenesis.
- Regenerative Response: Following liver injury, TGF-β signaling initially promotes an inflammatory response and later aids in the resolution of inflammation. Concurrently, the HIPPO pathway restricts excessive cell proliferation to maintain tissue homeostasis. The balance between these pathways is crucial for effective liver regeneration.
Role in Liver Diseases
Disruptions in the regulation of TGF-β and HIPPO pathways contribute to liver diseases. In fibrosis, the TGF-β pathway promotes the activation of hepatic stellate cells, leading to extracellular matrix deposition and scar formation. The HIPPO pathway’s dysregulation can result in uncontrolled cell proliferation, contributing to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Understanding the molecular interactions between these pathways provides insights into the mechanisms underlying liver disease progression and potential therapeutic targets.
- Fibrosis: Chronic liver injury triggers persistent TGF-β signaling, leading to the activation of hepatic stellate cells and excessive extracellular matrix production. This process results in fibrosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue that disrupts liver function.
- Liver Cancer: Dysregulation of the HIPPO pathway, particularly the overactivation of YAP/TAZ, has been implicated in the development of liver cancer. Uncontrolled YAP/TAZ activity promotes cell proliferation and survival, contributing to tumor growth and progression.
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process is crucial for liver wound healing and cancer metastasis. TGF-β is a potent inducer of EMT, promoting cell migration and invasion. The HIPPO pathway can modulate EMT by regulating YAP/TAZ activity. The interplay between these pathways influences EMT dynamics, impacting liver regeneration and disease progression.
- EMT in Liver Regeneration: During liver regeneration, TGF-β-induced EMT facilitates the migration and proliferation of liver progenitor cells, aiding in tissue repair. However, excessive or prolonged EMT can lead to fibrosis and impair liver function.
- EMT in Cancer: In liver cancer, TGF-β-driven EMT contributes to tumor metastasis by enabling cancer cells to acquire invasive properties. The HIPPO pathway’s regulation of YAP/TAZ activity can either suppress or promote EMT, depending on the cellular context.
Conclusions
The TGF-β and HIPPO signaling pathways are integral to liver physiology, influencing development, regeneration, and disease. Their intricate interplay regulates various cellular processes, from development to adulthood, and their dysregulation contributes to liver pathologies. Understanding these molecular interactions offers potential avenues for therapeutic interventions, aiming to restore liver function and prevent disease progression. The review provides comprehensive insights into the TGF-β and HIPPO pathways’ roles in maintaining liver health and their implications in liver diseases.
By examining the roles of these pathways in liver regeneration and disease, researchers can identify novel therapeutic targets to modulate their activity. For instance, targeting TGF-β signaling may help reduce fibrosis, while modulating the HIPPO pathway could prevent uncontrolled cell proliferation in liver cancer. Future studies should focus on elucidating the detailed mechanisms of TGF-β and HIPPO pathway interactions and their implications for liver health and disease management.
Full text
The study was recently published in the Gene Expression.
Gene Expression (GE) is an open-access journal. It was launched in 1991 by Chicago Medical School Press, and transferred to Cognizant Communication Corporation in 1994. From August 2022, GE is published by Xia & He Publishing Inc.
GE publishes peer-reviewed and high-quality original articles, reviews, editorials, commentaries, and opinions on its primary research topics including cell biology, molecular biology, genes, and genetics, especially on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of human diseases.
GE has been indexed in Medline (1991-2021), Scopus, Biological Abstracts, Biosis Previews, ProQuest, etc.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Gene Expression
Article Title
TGF-β and HIPPO Signaling Pathways Interplay in Distinct Hepatic Contexts
Article Publication Date
30-Jun-2024