Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, known as microrobots, capable of swimming through the lungs to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to metastatic tumors. This approach has shown promise in mice, where it inhibited the growth and spread of tumors that had metastasized to the lungs, thereby boosting survival rates compared to control treatments.

Credit: Zhengxing Li
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, known as microrobots, capable of swimming through the lungs to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to metastatic tumors. This approach has shown promise in mice, where it inhibited the growth and spread of tumors that had metastasized to the lungs, thereby boosting survival rates compared to control treatments.
The findings are detailed in a paper published on June 12 in Science Advances.
The microrobots are an ingenious combination of biology and nanotechnology. They are a joint effort between the labs of Joseph Wang and Liangfang Zhang, both professors in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.
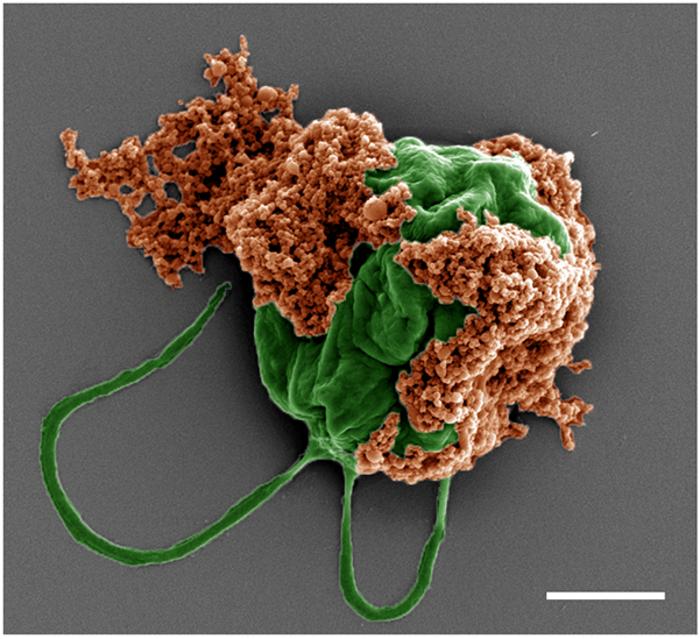
To create the microrobots, researchers chemically attached drug-filled nanoparticles to the surface of green algae cells. The algae, which provide the microrobots with their movement, enable the nanoparticles to efficiently swim around in the lungs and deliver their therapeutic payload to tumors.
The nanoparticles are made of tiny biodegradable polymer spheres, which are loaded with the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin and coated with red blood cell membranes. This coating serves a critical function: it protects the nanoparticles from the immune system, allowing them to stay in the lungs long enough to exert their anti-tumor effects. “It acts as a camouflage,” said study co-first author Zhengxing Li, who is a nanoengineering Ph.D. student in both Wang and Zhang’s research groups. “This coating makes the nanoparticle look like a red blood cell from the body, so it will not trigger an immune response.”
This formulation of nanoparticle-carrying algae is safe, the researchers noted. The materials used to make the nanoparticles are biocompatible while the green algae employed, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, are recognized as safe for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
This study builds on prior work by Wang and Zhang’s teams using similar microrobots to treat deadly pneumonia in mice. “Those were the first microrobots to be safely tested in the lungs of live animals,” said Wang.
In previous work, the microrobots fought the spread of pneumonia-causing bacteria using a different drug and cell membrane combination for the nanoparticles. By tweaking these components, the team has now tailored the microrobots to fight the spread of cancer cells in the lungs. “We demonstrate that this is a platform technology that can actively and efficiently deliver therapeutics throughout the entire lung tissue to combat different types of deadly diseases in the lungs,” said Zhang.
In the current study, mice with melanoma that had metastasized to the lungs were treated with the microrobots, which were administered to the lungs through a small tube inserted into the windpipe. Treated mice experienced a median survival time of 37 days, an improvement over the 27-day median survival time observed in untreated mice, as well as mice that received either the drug alone or drug-filled nanoparticles without algae.
“The active swimming motion of the microrobots significantly improved distribution of the drug to the deep lung tissue, while prolonging retention time,” said Li. “This enhanced distribution and prolonged retention time allowed us to reduce the required drug dosage, potentially reducing side effects while maintaining high survival efficacy.”
Moving forward, the team is working on advancing this microrobot treatment to trials in larger animals, with the ultimate goal of human clinical trials.
Paper: “Biohybrid microrobots locally and actively deliver drug-loaded nanoparticles to inhibit the progression of lung metastasis.” Co-authors of the study include Fangyu Zhang*, Zhongyuan Guo*, Zhengxing Li*, Hao Luan, Yiyan Yu, Audrey T. Zhu, Shichao Ding, Weiwei Gao and Ronnie H. Fang.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense (HDTRA1-21-1-0010) and the National Institutes of Health (R21AI175904).
Journal
Science Advances
Article Title
Biohybrid microrobots locally and actively deliver drug-loaded nanoparticles to inhibit the progression of lung metastasis
Article Publication Date
12-Jun-2024