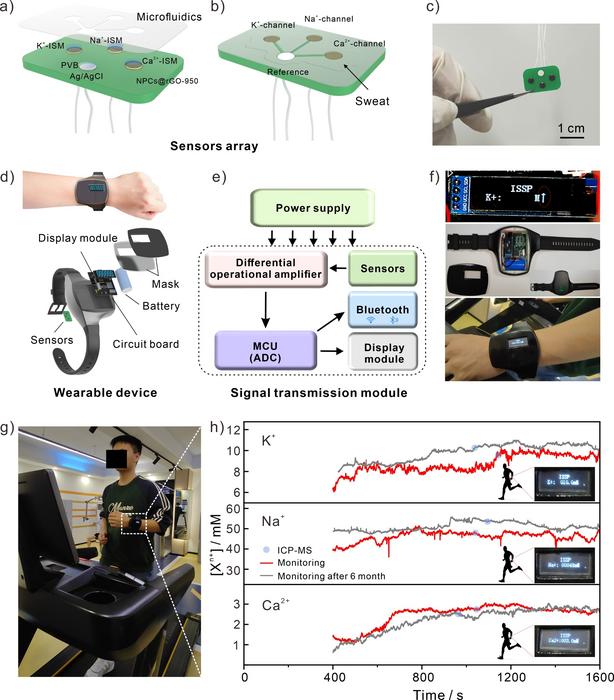
According to a research published in ACS Nano recently, a unique wristwatch has been created by a team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu from the Institute of Solid State Physics at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Solid contact (SC). Multiple modules, including a sensor array, a microfluidic chip, signal processing, and a data display system was packed in this advanced watch to monitor chemicals in human sweat.

Credit: CAI Xin
According to a research published in ACS Nano recently, a unique wristwatch has been created by a team led by Prof. HUANG Xingjiu from the Institute of Solid State Physics at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Solid contact (SC). Multiple modules, including a sensor array, a microfluidic chip, signal processing, and a data display system was packed in this advanced watch to monitor chemicals in human sweat.
“It can continuously and accurately monitor the levels of potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), and calcium (Ca2+) ions,” said Prof. HUANG, “offering both real-time and long-term tracking capabilities.”
Tremendous progress has been made in sweat sensors based on electrochemical methods, making it easier to track body changes. The stability of the sensor chip is crucial for its application effect and service life, which is the key to ensuring the long-term reliable operation of the sensor. Therefore, researchers focused on designing a stable SC interface as core components, while fully integrating multiple modules of the sweat sensor to achieve enable simultaneous and dependable monitoring of multiple target ions.
In this study, researchers developed mass-manufactured sensor arrays based on hierarchical multilayer-pore cross-linked N-doped porous carbon coated by reduced graphene oxide (NPCs@rGO-950) microspheres with high hydrophobicity as core SC. This enabled highly selective monitoring of K+, Na+, and Ca2+ ions in human sweat.
Using computed tomography and solid-solid interface potential diffusion simulation, they found that he diffusion of substances between solid interfaces is very low, and the ability to store electrical charge at these interfaces is high. This ensures the excellent potential stability, reversibility, repeatability, and selectivity of sensor arrays.
This watch’s long-term reliability is remarkable. It can consistently monitor the three ions in human sweat for over 6 months, surpassing the stability of many other sensors that have been reported.
This study represents a comprehensive approach to material design, interface mechanism research, mass production of sensor chips, and modular full integration, providing more possibilities for wearable electrochemical sweat sensors, according to the team.