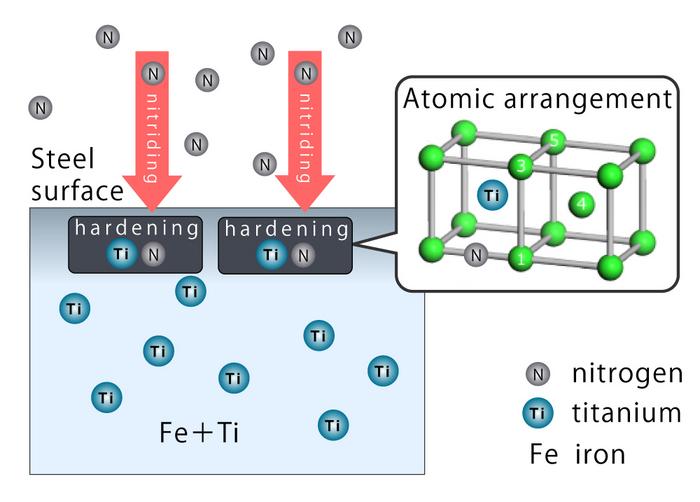
Decarbonization of automobiles not only requires a shift from gasoline engines to electric motors, but also quality steel parts that help the motors run while lessening the weight of vehicles. High-performance steel materials can offer quieter rides and resist the wear and tear from high-speed rotation in motors. To create them, the process of modifying the steel surface with carbon, nitrogen, and alloy elements needs to be optimized.

Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University
Decarbonization of automobiles not only requires a shift from gasoline engines to electric motors, but also quality steel parts that help the motors run while lessening the weight of vehicles. High-performance steel materials can offer quieter rides and resist the wear and tear from high-speed rotation in motors. To create them, the process of modifying the steel surface with carbon, nitrogen, and alloy elements needs to be optimized.
To understand the interactions between elements in steel, a systematic investigation has been conducted by an Osaka Metropolitan University research group led by Associate Professor Tokuteru Uesugi of the Graduate School of Informatics. The group theoretically calculated 120 combinations of how 12 alloy elements, including aluminum and titanium, interact with carbon during carburization and nitrogen in the nitriding process.
The results showed that when titanium is placed in a specific arrangement, it bonds with nitrogen or carbon, hardening the iron. The group’s analytical data also showed that the alloy element must have a larger metallic radius than the iron atom to bond well.
“Although it was not easy to elucidate the mechanism from the results of numerous calculations, we used multiple linear regression and stratified analysis through trial and error,” Professor Uesugi stated. “These results are expected to contribute to a better understanding of the mechanisms of steel strengthening and improved durability, and to the development of superior materials.”
The findings were published in ISIJ International.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
Journal
ISIJ International
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Interactions between interstitial and substitutional elements of solute diatomic and triatomic clusters in α-Fe from first-principles calculations
Article Publication Date
6-Apr-2024