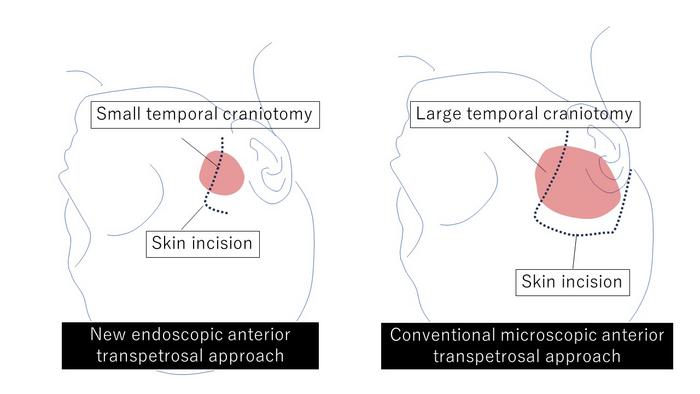
Tumors arising in the base of the skull are among the most difficult to remove in neurosurgery. The current treatment method is to perform surgical removal by what is known as the microscopic anterior transpetrosal approach (ATPA). Seeking to lessen the risk of damage and postoperative complications, as the skull base is densely packed with nerves, blood vessels, and other tissues, not to mention the brain stem, an Osaka Metropolitan University medical research team is taking a new approach.

Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University
Tumors arising in the base of the skull are among the most difficult to remove in neurosurgery. The current treatment method is to perform surgical removal by what is known as the microscopic anterior transpetrosal approach (ATPA). Seeking to lessen the risk of damage and postoperative complications, as the skull base is densely packed with nerves, blood vessels, and other tissues, not to mention the brain stem, an Osaka Metropolitan University medical research team is taking a new approach.
Led by Dr. Hiroki Morisako, a lecturer in the Graduate School of Medicine’s Department of Neurosurgery, and Professor Takeo Goto, who heads the department, the team has developed a minimally invasive surgical technique called a purely endoscopic subtemporal keyhole ATPA. The team members write in The Journal of Neurosurgery that this is, to their knowledge, the first time this procedure to remove lesions in the skull base region known as the petrous apex has been described in an article.
The endoscopic technique means a smaller area of the skull needs to be surgically opened compared to the microscopic approach, an average of only 11.2 cm² versus 33.9 cm². The risk of damage to the brain is also reduced.
The team performed 10 neurosurgeries using their method from 2022 to 2023 at Osaka Metropolitan University Hospital and compared the results to 13 surgeries using the microscopic ATPA from 2014 to 2021. In terms of operative time, the endoscopic approach reduced it noticeably, from an average of 410.9 minutes to 252.9 minutes. Similarly, blood loss lessened from a mean of 193 ml to 90 ml. The degree of tumor resection (surgical removal) was just as high as the microscopic method, while neurological functions were preserved at a rate equal to or higher than with the conventional approach.
“Comparison of the new endoscopic method and the conventional microscopic method showed no significant difference in tumor resection rate or in the ability to perform daily activities before and after surgery, with the new endoscopic approach resulting in shorter operative times and less blood loss,” Professor Goto stated. “The widespread use of this surgical procedure is expected to improve the treatment results of brain tumors in the base of the skull, not only in Japan but also worldwide.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
Journal
Journal of Neurosurgery
Method of Research
Case study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Purely endoscopic subtemporal keyhole anterior transpetrosal approach to access the petrous apex region: surgical techniques and early results
Article Publication Date
5-Apr-2024
COI Statement
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.