In a groundbreaking advancement that pushes the boundaries of machine vision technology, researchers at Fuzhou University in China have engineered a novel visual sensor capable of adapting to drastic changes in lighting significantly faster than the human eye. Published in the journal Applied Physics Letters on July 1, 2025, this innovative device exploits the exceptional properties of quantum dots—nanoscale semiconductors engineered to replicate the adaptive mechanisms intrinsic to biological eyes. This development holds the promise to revolutionize the safety and reliability of autonomous systems operating in environments where lighting conditions are highly variable.
Human vision is a marvel of biological engineering. Whether transitioning from the blinding brightness of midday sun to the deepest darkness of night or vice versa, our eyes, in conjunction with the neurons and brain, recalibrate visual sensitivity within several minutes. Not only does this system exhibit dynamic adjustment to ambient light, but it also leverages learned experiences, speeding adaptation in familiar lighting environments. The sensor developed by the Fuzhou University team mimics this biological sophistication, achieving light adaptation in approximately 40 seconds—an astonishing feat given that most existing artificial vision systems require significantly longer or lack such adaptive flexibility.
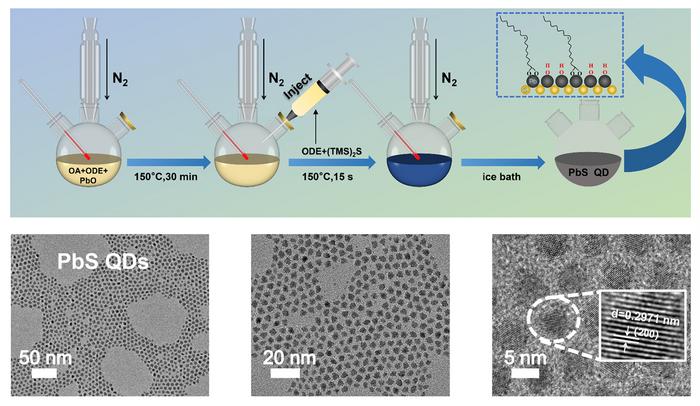
Central to this breakthrough is the utilization of lead sulfide quantum dots embedded in a multilayered structure of polymers and zinc oxide. Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor particles that can efficiently convert incident photons into electrical signals, but the innovation here lies in their engineered ability to selectively trap and release electrical charges based on environmental illumination. This mechanism closely resembles how photoreceptor cells in the human retina store and regulate light-sensitive pigments, a capability that enables the eye to adjust sensitivity when moving between bright and dim environments. By designing the quantum dots to act like a "charge sponge," the device momentarily holds trapped charges during intense light exposure and strategically releases them when lighting dims, facilitating rapid and dynamic response.
This bio-inspired sensor architecture also integrates specialized electrode configurations that enhance its responsiveness. The layered assembly ensures that the sensor’s electrical characteristics vary optimally with changes in incident light intensity. When exposed to bright light, excess charges are trapped within the quantum dot layers, preventing sensor saturation and preserving its operational range. Conversely, in low-light conditions, the stored charges are released, elevating the sensor’s sensitivity—akin to the enhancement seen in living eyes adapting to darkness, known as dark adaptation. This intricate interplay results in a device whose performance surpasses existing machine vision sensors both in speed and energy efficiency.
Perhaps just as important as its rapid response is the sensor’s ability to drastically reduce redundant data generation, a common challenge in modern machine vision systems. Traditional imaging technologies indiscriminately capture vast quantities of visual information, much of which may be irrelevant, imposing heavy computational burdens and increased power consumption. Inspired by the human retina’s data preprocessing capabilities, the quantum dot sensor intelligently filters and processes light information at the source. This selective perception dramatically trims unnecessary data before transmission, enhancing system efficiency and potentially enabling lower-power operation in autonomous vehicles and robotics.
At the core of this achievement is the seamless fusion of nanotechnology with neuroscientific principles. By bridging these disciplines, the research team has crafted a sensory platform that not only imitates but improves upon biological vision in critical operational parameters. The approach underlines a growing trend in engineering to design devices that transcend mere electronic replication by incorporating nuanced behavioral functionalities observed in living organisms. This translational science opens new avenues in the development of smart sensors with unprecedented adaptability and intelligence.
Looking ahead, the researchers anticipate scaling their prototype sensor into larger arrays integrated with edge-AI chips. Edge-AI technology allows data processing and decision-making to occur directly on the sensor hardware, significantly minimizing latency and bandwidth requirements. The marriage of quantum dot sensor arrays with onboard artificial intelligence promises a transformative impact on autonomous driving, where rapid real-time interpretation of dynamic scenes under varying lighting is critical for safety and performance. Such systems would excel in challenging situations encountered by self-driving cars, such as abruptly moving from sunlit highways into dark tunnels or underpasses.
The potential applications extend beyond automotive technology. Alternatively, this adaptive sensor could empower next-generation robots executing precision tasks in environments where lighting is unpredictable. From industrial automation to exploratory devices operating in dim or fluctuating illumination, this sensor offers a robust visual foundation that can enhance machine perception. Moreover, its low power profile aligns well with the growing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient embedded systems.
The significance of this innovation reflects a broader paradigm shift in sensor design—highlighting the value of biomimicry and nanoscale engineering in creating devices that not only function but think like natural systems. By emulating how visual neurons preprocess and modulate stimuli, this device overcomes long-standing hurdles of adaptability and data overload. The resulting technology could well mark a pivotal moment in the evolution of machine vision, pushing autonomous systems closer to the seamless responsiveness of biological perception.
Despite the impressive technical achievements, the research team acknowledges future challenges. Integrating such quantum dot-based sensors with existing vehicle architectures will require thorough systems engineering to ensure compatibility and reliability. Additionally, optimizing sensor arrays for mass production while preserving fine-tuned charge manipulation remains a key engineering hurdle. Nonetheless, early results provide a promising roadmap toward commercial viability.
To conclude, this bio-inspired quantum dot visual sensor stands as a testament to the power of interdisciplinary science. By meticulously engineering nanoscale materials that incorporate the dynamic charge storage and release behaviors found in human photoreceptors, the researchers have crafted a device that adapts to light changes faster and more efficiently than ever before. Such capability is poised to redefine machine vision applications, making autonomous vehicles safer and robots more perceptive in rapidly shifting environments.
Subject of Research: Development of a bio-inspired nanoscale visual sensor using quantum dots for rapid adaptive perception
Article Title: A back-to-back structured bionic visual sensor for adaptive perception
News Publication Date: July 1, 2025
Web References:
https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0268992
https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl
References:
Lin, X., Lin, Z., Zhao, W., Xu, S., Chen, E., Guo, T., Ye, Y. (2025). A back-to-back structured bionic visual sensor for adaptive perception. Applied Physics Letters. DOI: 10.1063/5.0268992
Image Credits: Lin et al.
Keywords
Robotics, Engineering, Physics, Robotic Sensors, Light Sensors