MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (05/02/2024) — For the first time, chemists in the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics.

Credit: The Roberts Group/University of Minnesota
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (05/02/2024) — For the first time, chemists in the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering have created a highly reactive chemical compound that has eluded scientists for more than 120 years. The discovery could lead to new drug treatments, safer agricultural products, and better electronics.
For decades, researchers have been investigating molecules called N-heteroarenes, which are ring-shaped chemical compounds that contain one or more nitrogen atoms. Bio-active molecules having a N-heteroarene core are widely used for numerous medicinal applications, lifesaving pharmaceuticals, pesticides and herbicides, and even electronics.
“While the average person does not think about heterocycles on a daily basis, these unique nitrogen-containing molecules are widely applied across all facets of human life,” said Courtney Roberts, the senior author of the study and a University of Minnesota Department of Chemistry assistant professor who holds the 3M Alumni Professorship.
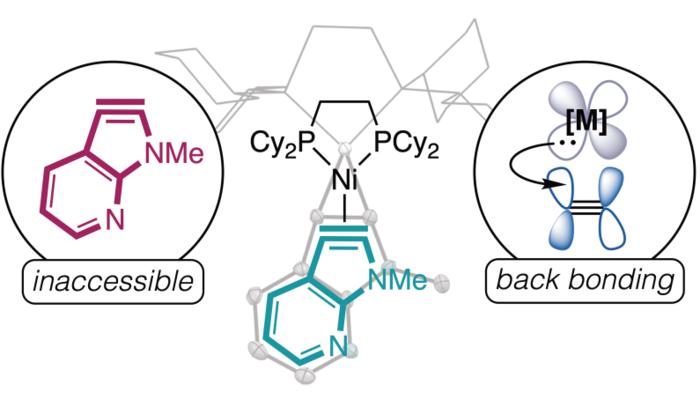
These molecules are highly sought out by many industries, but are extremely challenging for chemists to make. Previous strategies have been able to target these specific molecules, but scientists have not been able to create a series of these molecules. One reason for this is that these molecules are extremely reactive. They are so active that chemists have used computational modeling to predict that they should be impossible to make. This has created challenges for more than a century and prevented a solution to create this chemical substance.
“What we were able to do was to run these chemical reactions with specialized equipment while getting rid of elements commonly found in our atmosphere,” said Jenna Humke, a University of Minnesota chemistry graduate student and lead author on the paper. “Luckily, we have the tools to do that at the University of Minnesota. We ran experiments under nitrogen in a closed-chamber glovebox, which creates a chemically inactive environment to test and move samples.”
These experiments were accomplished by using organometallic catalysis—the interaction between metals and organic molecules. The research required collaboration between both organic and inorganic chemists. This is something that is common at the University of Minnesota.
“We were able to solve this long-standing challenge because the University of Minnesota Department of Chemistry is unique in that we don’t have formal divisions,” Roberts added. “This allows us to put together a team of experts in all fields of chemistry, which was a vital component in completing this project”
After introducing the chemical compound in this paper, the next steps will be to make it widely available to chemists across multiple fields to streamline the creation process. This could help solve important problems like preventing food scarcity and treating illnesses to save lives.
Along with Roberts and Humke, the University of Minnesota research team included postdoctoral researcher Roman Belli, graduate students Erin Plasek, Sallu S. Kargbo, and former postdoctoral researcher Annabel Ansel.
This work was primarily funded by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation. Funding was also provided by four University of Minnesota-sponsored graduate research fellowships and start-up funding provided by the Department of Chemistry.
To read the entire research paper titled, “Nickel binding enables isolation and reactivity of previously inaccessible 7-Aza-2,3-indolynes”, visit the Science website.
Journal
Science
Article Title
Nickel binding enables isolation and reactivity of previously inaccessible 7-Aza-2,3-indolynes
Article Publication Date
26-Apr-2024