(LOS ANGELES, July 30, 2024) – An extensive analytical study performed at the Terasaki Institute and published in Frontiers in Immunology highlights the crucial role of tissue-resident memory T cells and how they influence the immune environment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their overall prognosis.

Credit: Terasaki Institute
(LOS ANGELES, July 30, 2024) – An extensive analytical study performed at the Terasaki Institute and published in Frontiers in Immunology highlights the crucial role of tissue-resident memory T cells and how they influence the immune environment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their overall prognosis.
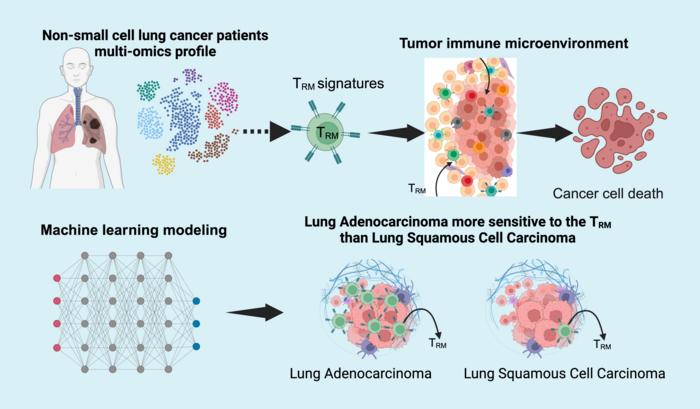
Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for ~85% of lung tumors and is a leading cause of death in adults. Tissue-resident memory T cells, a specialized subset of immune cells residing in peripheral tissues, have been suspected of impacting cancer progression. However, it’s still not fully understood how tissue-resident memory T cells affect the tumor immune microenvironment and tumor progression in various non-small cell lung cancer patient populations.
In this comprehensive study, multiple independent datasets from lung cancer patient samples were analyzed. In addition, a machine learning model was developed and validated to predict patient survival, refining an 18-gene risk score that effectively categorizes lung cancer patients into low-risk and high-risk groups. In cancer research, the 18-gene risk score is used to predict disease progression or recurrence chances, which helps create personalized treatment plans. The scores are usually divided into low and high risk, with specific thresholds setting these categories. In this study, patients with high-risk scores exhibited significantly lower overall survival rates than their low-risk counterparts. Distinct Tissue Resident Memory T cell biomarkers were identified that correlate positively with other immune cells within the tumor environment. Moreover, these biomarkers were strongly associated with immune checkpoint and stimulatory genes, directly influencing patient prognosis.
“The study’s findings highlight the critical impact of Tissue Resident Memory T cell abundance on immune responses and patient outcomes in lung cancer,” said Dr. Xiling Shen, Chief Scientific Officer at Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation. “Our findings not only validate these cells as a prognostic marker but also underscore their potential in guiding personalized treatment strategies, particularly in immunotherapy.”
This pioneering research, independently validated by the Cancer Genome Atlas Program and multiple lung cancer patient datasets, provides a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between Tissue Resident Memory T cells and the tumor. It represents a significant step towards advancing precision medicine in lung cancer treatment.
Authors: Aidan Shen, Aliesha Garrett, Cheng-Chi Chao , Dongliang Liu, Chao Cheng, Zhaohui Wang, Chen Qian, Yangzhi Zhu, Junhua Mai, Chongming Jiang
Grant Information: The author(s) declare financial support was received for the
research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is
supported by the National Institutes of Health, United States (NIH)
For more information, please visit Terasaki.org or Contact:
Stewart Han
Email: shan@terasaki.org
Chongming Jiang
Email: tom.jiang@terasaki.org
###
About Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is a non-profit research organization dedicated to leveraging cutting-edge technology to address global health challenges. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations and pushing the boundaries of innovation, TIBI aims to transform healthcare and improve lives worldwide.
Journal
Frontiers in Immunology
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
A comprehensive meta-analysis of tissue resident memory T cells and their roles in shaping immune microenvironment and patient prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer
Article Publication Date
8-Jul-2024
COI Statement
Author C-CC was employed by the company Biomap, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.