Plastic pollution presents a global challenge that must be solved. In particular, packaging accounts for 30-50% of the total plastic consumption. While paper packaging is eco-friendly, it lacks crucial functionalities like moisture resistance and strength. Traditional coating materials exacerbate plastic pollution, prompting the need for sustainable alternatives.

Credit: KAIST Waste-Innovating Technologies for Humanity Laboratory (WITHLAB)
Plastic pollution presents a global challenge that must be solved. In particular, packaging accounts for 30-50% of the total plastic consumption. While paper packaging is eco-friendly, it lacks crucial functionalities like moisture resistance and strength. Traditional coating materials exacerbate plastic pollution, prompting the need for sustainable alternatives.
Polyethylene (PE) and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) are typically used as coating materials to improve the low barrier properties of paper packaging, but these substances do not decompose and worsen microplastic pollution when disposed of in the natural environment. In response to this problem, packaging materials made from bio-based substances and biodegradable plastics have been developed, but in most cases, as the packaging performance improves, the biodegradability diminishes rapidly.
KAIST announced that a joint research team led by Professor Jaewook Myung of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Professor Hanseul Yang of the Department of Life Sciences, and Professor Jongcheol Seo of the Department of Packaging and Logistics at Yonsei University tackled the challenge of balancing packaging performance and sustainability. They successfully developed a sustainable, marine biodegradable, high-performance paper coating material.
* Biodegradable plastic: A plastic that can be decomposed by microorganisms in natural environments such as soil and ocean or artificial conditions such as industrial composting and anaerobic digestion by microorganisms.
*Microplastics: Tiny pieces of plastic less than 5 mm, produced during the decomposition of bulk plastic materials. Microplastics can persist in the sea for more than decades, causing severe marine pollution.
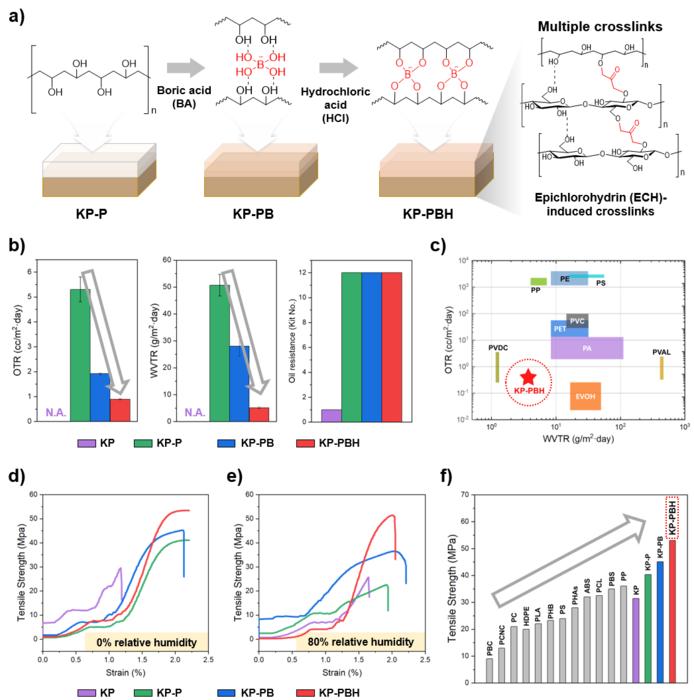
The team utilized boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), a biodegradable plastic, to coat the paper, thereby enhancing its biodegradability, barrier properties, and strength. The resulting coated paper exhibited superior performance compared to conventional plastics, with excellent barrier properties and physical strength, even in humid conditions.
The team also conducted an in-depth examination of biodegradation and biocompatibility to systematically evaluate the sustainability of the newly developed coated paper. Biodegradation was assessed by simulating the marine environment, known for its challenging biodegradability conditions. The team employed a respiratory system-based bioreactor to measure the degree of carbon mineralization into carbon dioxide. After 111 days of biodegradation, it was found that the coated papers achieved 59-82% biodegradation depending on the coating component. The phenomenon in which marine bacteria are decomposing the coating material was captured through a scanning electron microscope. In addition, in vitro biocompatibility was confirmed through human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, as well as high in-vivo biocompatibility of the coated paper was verified through mouse experiments.
Through this study, the joint research team proposed a coating strategy that can improve packaging performance while upholding sustainability to address the drawbacks of paper packaging. The boric acid-crosslinked PVA-coated paper eliminates the need for artificial composting conditions or sewage treatment facilities. Being biodegradable in natural environments and characterized by low toxicity, this newly coated paper does not exacerbate environmental pollution when accidentally discarded. Thus, it presents a sustainable substitute for plastic packaging materials.
Professor Jaewook Myung at KAIST, who led the sustainability study of coated paper, said, “The development of a marine biodegradable high-performance paper coating is the result of combining the innovative technologies of three leading research teams in each field.” He said, “We will continue to develop sustainable materials with excellent performance.” Meanwhile, Professor Jongchul Seo of Yonsei University, who led the research on the development of high-performance paper coating, mentioned, “Through this research, we have developed a sustainable paper packaging technology that can replace non-degradable plastic packaging, and we expect the research outcome will be applied in industry,”.
The work was published in Green Chemistry and Food Chemistry journals. This study was conducted with the support of the Korea Research Foundation and the Korea Institute for Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Technology Planning and Evaluation, etc.
*Title of paper published in Green Chemistry: Boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol): biodegradable, biocompatible, robust, and high-barrier paper coating
※ Selected as the article for the back cover of the journal .
– Authors: Shinhyeong Choe, Seulki You, Kitae Park, Youngju Kim, Jehee Park, Yongjun Cho, Jongchul Seo, Hanseul Yang, and Jaewook Myung)
– Date: April 17, 2024
– DOI: 10.1039/D4GC00618F
*Title of paper published in Food Chemistry: Effect of epichlorohydrin treatment on the coating process and performance of high-barrier paper packaging
– Authors: Kitae Park, Shinhyeong Choe, Kambiz Sadeghi, Pradeep Kumar Panda, Jaewook Myung, Dowan Kim, and Jongchul Seo
– Date: February 19, 2024
– DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138772
Journal
Green Chemistry
Method of Research
Meta-analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol): biodegradable, biocompatible, robust, and high-barrier paper coating
Article Publication Date
17-Apr-2024
COI Statement
N/A