Philadelphia, June 17, 2024 – Early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)—one of the most fatal malignancies—is crucial to improve patient survival. In a breakthrough study investigators report on the development of a serum fusion-gene machine-learning model. This important screening tool may increase the five-year survival rate of patients with HCC from 20% to 90% because of its improved accuracy in early diagnosis of HCC and monitoring the impact of treatment. The study appears in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier.

Credit: The American Journal of Pathology
Philadelphia, June 17, 2024 – Early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)—one of the most fatal malignancies—is crucial to improve patient survival. In a breakthrough study investigators report on the development of a serum fusion-gene machine-learning model. This important screening tool may increase the five-year survival rate of patients with HCC from 20% to 90% because of its improved accuracy in early diagnosis of HCC and monitoring the impact of treatment. The study appears in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier.
HCC is the most common form of liver cancer and accounts for around 90% of cases. Currently, the most common screening test for the HCC biomarker, serum alpha-fetal protein, is not always accurate, and up to 60% of liver cancers are only diagnosed in advanced stages, resulting in a survival rate of only around 20%.
Lead investigator Jian-Hua Luo, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, High Throughput Genome Center, and Pittsburgh Liver Research Center, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, explained: “Early diagnosis of liver cancer helps save lives. However, most liver cancers occur insidiously and without many symptoms. This makes early diagnosis challenging. What we need is a cost-effective, accurate, and convenient test to screen early-stage liver cancer in human populations. We wanted to explore if a machine-learning approach could be used to increase the accuracy of screening for HCC based on the status of the fusion genes.”
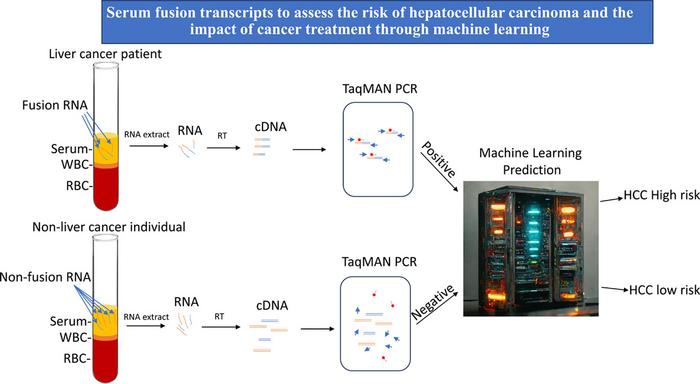
In the search for a more effective and efficient diagnostic tool to predict non-HCC and HCC cases, investigators analyzed a panel of nine fusion transcripts in serum samples from 61 patients with HCC and 75 patients with non-HCC conditions using real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). Seven of the nine fusions were frequently detected in HCC patients. The researchers generated machine-learning models based on serum fusion-gene levels to predict HCC in the training cohort, using the leave-one-out cross-validation approach.
A four fusion gene logistic regression model produced an accuracy of 83% to 91% in predicting the occurrence of HCC. When combined with serum alpha-fetal protein, the two-fusion gene plus alpha-fetal protein logistic regression model produced 95% accuracy for all the cohorts. Furthermore, quantification of fusion gene transcripts in the serum samples accurately assessed the impact of the treatment and was able to monitor for the recurrence of the cancer.
Dr. Luo commented, “The fusion gene machine-learning model significantly improves the early detection rate of HCC over the serum alpha-fetal protein alone. It may serve as an important tool in screening for HCC and in monitoring the impact of HCC treatment. This test will find patients who are likely to have HCC.”
Dr. Luo concluded, “Early treatment of liver cancer has a 90% five-year survival rate, while late treatment has only 20%. The alternative to this test is to subject every individual with some risk of liver cancer to imaging analysis every six months, which is very costly and ineffective. In addition, when imaging results are ambiguous, this test will help to differentiate malignant versus benign lesions.”
Journal
American Journal Of Pathology
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Serum Fusion Transcripts to Assess the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and the Impact of Cancer Treatment Through Machine Learning