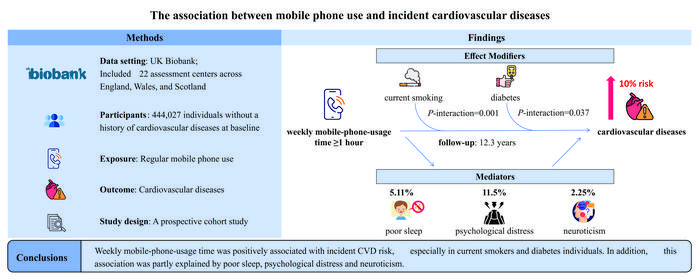
Philadelphia, September 4, 2024 – A new study has found that regular mobile phone use was positively associated with incident cardiovascular diseases risk, especially in current smokers and individuals with diabetes. In addition, this association was partly attributed to poor sleep, psychological distress, and neuroticism. The article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the results of this large-scale prospective cohort study.

Credit: Canadian Journal of Cardiology
Philadelphia, September 4, 2024 – A new study has found that regular mobile phone use was positively associated with incident cardiovascular diseases risk, especially in current smokers and individuals with diabetes. In addition, this association was partly attributed to poor sleep, psychological distress, and neuroticism. The article in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, details the results of this large-scale prospective cohort study.
Yanjun Zhang, MD, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, explains, “Mobile phone use is a ubiquitous exposure in modern society, so exploring its impact on health has significant public health value. Radio-frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF) emitted by mobile phones cause dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress, and are therefore expected to affect a variety of organs such as the heart and blood vessels. However, whether mobile phone use is associated with the risk of cardiovascular diseases remains uncertain.”
Co-investigator Ziliang Ye, MD, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, adds, “We aimed to assess the prospective association of regular mobile phone use with incident cardiovascular diseases and explore the mediating effects of sleep and mental health. We found that compared with non-regular mobile phone users, regular mobile phone users had a significantly higher risk of incident cardiovascular diseases.”
The study included 444,027 individuals from the UK Biobank without a history of cardiovascular diseases who self-reported on the frequency of their mobile phone use from 2006 to 2010. Regular mobile phone use was defined as at least one call per week. Using linked hospital and mortality records, the composite outcome of incident stroke, coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure was ascertained over a median followup time of 12.3 years. Researchers also investigated the role of sleep patterns, psychological distress, and neuroticism.
Co-investigator Xianhui Qin, MD, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, notes, “We found that sleep patterns, psychological distress, and neuroticism may be potential mechanisms of the association between mobile phone use and cardiovascular diseases. A poor sleep pattern and poor mental health may adversely affect the development of cardiovascular diseases through disrupted circadian rhythm, endocrine and metabolic disruption, and increased inflammation. In addition, chronic exposure to RF-EMF radiation emitted from mobile phones could lead to oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Therefore, RF-EMF radiation exposure from mobile phones in combination with smoking and diabetes may have a synergistic effect in increasing cardiovascular diseases risk.”
An accompanying editorial contextualizes the findings of the study. Given that the recruitment window of this study (2006-2010) occurred before the widespread use of modern smartphones, which are now more commonly used for other activities (e.g., entertainment, text messaging/email, social networking, etc.), the generalizability and current relevance of these findings require careful consideration.
Co-author of the editorial Nicholas Grubic, MSc, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, ON, Canada, concludes, “While the current study suggests that using a mobile phone may moderately increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, more conclusive evidence with valid measurements of mobile phone use is needed before this association becomes a concern for the general public. Maintaining responsible mobile phone habits should be a valuable component of an all-encompassing approach to supporting cardiovascular health. Before diving into hours of mindless ’doom-scrolling’ on your smartphone today, consider redirecting this time toward a more heart-healthy activity.”
Journal
Canadian Journal of Cardiology
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Regular Mobile Phone Use and Incident Cardiovascular Diseases: Mediating Effects of Sleep Patterns, Psychological Distress, and Neuroticism
Article Publication Date
4-Sep-2024