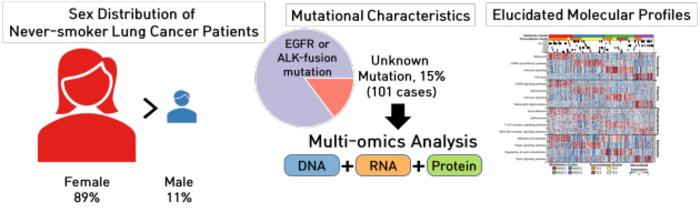
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. However, the incidence of lung cancer among never-smokers has been steadily increasing, especially among women. While approximately 80% of never-smoking lung cancer patients are prescribed targeted therapies that focus on mutations in proteins such as EGFR and ALK, the remaining patients often receive cytotoxic chemotherapy with high side effects and relatively low response rates, highlighting the urgent need for targeted therapies.

Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. However, the incidence of lung cancer among never-smokers has been steadily increasing, especially among women. While approximately 80% of never-smoking lung cancer patients are prescribed targeted therapies that focus on mutations in proteins such as EGFR and ALK, the remaining patients often receive cytotoxic chemotherapy with high side effects and relatively low response rates, highlighting the urgent need for targeted therapies.
Dr. Lee Cheolju’s team at the Chemical Life Convergence Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), along with Dr. Kim Seon-Young’s team at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology and Dr. Han Ji-Youn’s team at the National Cancer Center, have elucidated the overexpression of estrogen signaling pathways in specific Korean never-smoking lung cancer cases using multi-omics analysis and proposed the anti-cancer drug saracatinib as a targeted therapeutic agent. Multi-omics integrates various molecular information, with proteomics presenting a particular challenge due to the need to analyze small amounts of proteins without loss, typically microgram-scale.
The research team obtained tissue samples from 101 Korean never-smoking lung cancer patients without identified treatment targets among 1,597 patients who visited the National Cancer Center over the past decade and distributed clinical information, genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic data to each omics analysis method for mutual referencing. Particularly, proteomic analysis measured an average of over 9,000 proteins and 5,000 phosphorylated proteins per sample using only 100 μg of protein, which is 10% of the amount required for conventional protein analysis, using isotopic labeling techniques.
Analysis of genetic mutations and cellular signaling pathways revealed that driver mutations of genes known to be associated with cancer, such as STK11 and ERBB2, were observed in the tissues of never-smoking lung cancer patients. Additionally, while the estrogen signaling pathway was found to be overexpressed, there were no significant changes in estrogen hormone receptors. Based on this, saracatinib, a sub estrogen signaling transduction protein inhibitor, showed statistically significant (p<0.01) cell death effects when applied to cells with mutations in STK11 and ERBB2 compared to the control group without such mutations.
Building on this, the research team is developing a molecular diagnostic technique for discriminating patients with specific expression of estrogen signaling pathways among never-smoking lung cancer patients. Additionally, they plan to conduct preclinical trials of saracatinib’s therapeutic effects on never-smoking lung cancer animal models in collaboration with the National Cancer Center.
Dr. Lee Cheolju of KIST stated, “This successful case of discovering new therapeutic targets for refractory cancer through multi-omics analysis is based on purely domestic research and the collaborative efforts of hospitals and research institutions, which holds significant meaning. Building on this experience, we will lead the expansion of multi-omics research on human diseases.”
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea, under the KIST’s main projects and the Bio-Medical Technology Development Program (2022M3H9A2096187). The research results have been published online in the latest issue of the international journal Cancer Research (IF 11.2, JCR field 10.6%).
Journal
Cancer Research
Article Title
Proteogenomic Characterization Reveals Estrogen Signaling as a Target for Never-Smoker Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients without EGFR or ALK Alterations
Article Publication Date
15-Apr-2024