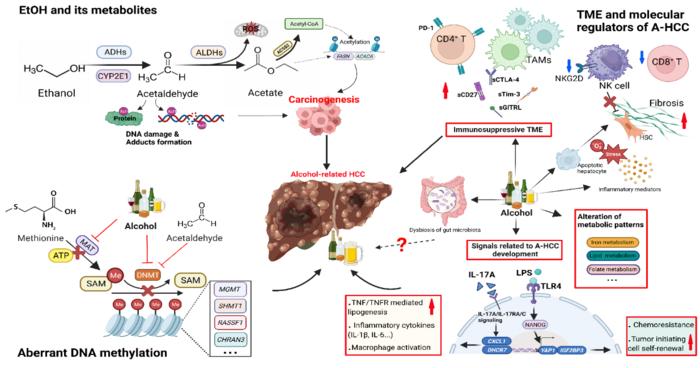
While heavy drinking is a well-established risk factor for liver cancer, the specific mechanisms by which alcohol contributes to A-HCC remain unclear.

Credit: By Fu, Yaojie, Maccioni, Luca, Wang, Xin Wei, Greten, Tim F, Gao, Bin.
While heavy drinking is a well-established risk factor for liver cancer, the specific mechanisms by which alcohol contributes to A-HCC remain unclear.
This insightful review, published in Hepatology, provides a comprehensive summary of the pathogenesis, heterogeneity, preclinical approaches, epigenetic and genetic profiles of A-HCC. Compared to other types of liver cancer, A-HCC is often diagnosed at a later stage, when the disease is more advanced. This is partly due to a lack of readily available screening tools for individuals with alcohol-related liver disease (ALD).
“A-HCC is a serious public health concern,” says Yaojie Fu, lead author of the review. “Our work highlights the importance of understanding how alcohol and its metabolites contribute to this aggressive form of liver cancer. By investigating the unique characteristics of A-HCC, we hope to develop better diagnostic tools and treatment options.”
There is a strong connection between alcohol consumptions and the risk of A-HCC. People who drink heavily are at a much higher risk of developing this aggressive form of liver cancer. However, the exact reasons why alcohol contributes to A-HCC are not fully understood. Compared to HCC of other etiologies, A-HCC is often diagnosed at a later stage, when the disease is more advanced. This can be attributed to the lack of readily available screening approaches for individuals with ALD. In this regard, the authors proposed that HCC screening and surveillance among patients with alcohol-related cirrhosis, and more accurate methods of risk stratification are critical for the early intervention of A-HCC.
In this review, the authors also discussed the potential role of genetics in A-HCC development. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of some specific genes can modify the risk of alcohol related cirrhosis and susceptibility of A-HCC. However, more studies are warranted to decipher the potential mechanisms of how SNPs impact the progression of A-HCC.
More importantly, the review also emphasizes the molecular mechanisms and the heterogeneity of A-HCC. Developing better preclinical models is crucial for a deeper understanding of characteristics, as well as prevention and personalized therapeutics of A-HCC clinically.
See the article:
Fu Y, Maccioni L, Wang XW, Greten TF, Gao B. Alcohol-associated liver cancer. Hepatology. 2024 Apr 12. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000890. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38607725.