Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.

Credit: Shaban Alizadeh, Ziba Majidi
Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.
Role of m6A Modification in Leukemia
m6A Writers and Erasers
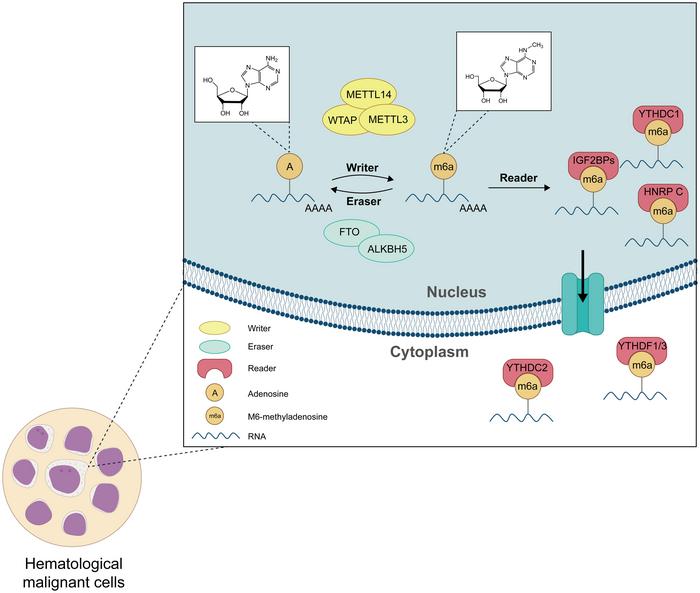
m6A modifications are mediated by “writers” (e.g., METTL3, METTL14, and WTAP) that catalyze the methylation of adenosine residues in RNA, and “erasers” (e.g., ALKBH5 and FTO) that remove these methyl groups. These enzymes play crucial roles in regulating the balance of m6A levels in leukemia cells.
Recent studies have demonstrated that dysregulation of m6A writers and erasers can significantly impact leukemia development and progression. For instance, knockdown of METTL3 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) leads to reduced cell growth and increased myeloid differentiation, whereas METTL14 depletion impairs self-renewal capacity of HSPCs and promotes myeloid differentiation.
Functional Implications
m6A modifications affect various aspects of RNA metabolism, including splicing, stability, translation, and subcellular localization. In leukemia, these modifications have been shown to regulate cell differentiation, proliferation, and self-renewal capacity. For example, m6A-modified mRNAs involved in hematopoiesis are differentially expressed in leukemic cells, leading to disrupted hematopoiesis and enhanced leukemogenesis.
Specific Leukemia Types
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): m6A modifications have been implicated in the pathogenesis of AML. Studies have shown that upregulation of m6A writers and demethylases correlates with disease progression and chemoresistance. Conversely, inhibition of these enzymes has shown therapeutic potential in preclinical models.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): ALL, the most prevalent cancer in children under 15 years, also exhibits dysregulation of m6A modifications. Elevated levels of m6A writers and demethylases have been observed in pediatric ALL patients, particularly those with specific immune cell phenotypes.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): CML is characterized by a translocation event that generates the BCR-ABL1 fusion oncogene. m6A modifications have been shown to regulate BCR-ABL1 expression and downstream signaling pathways, affecting CML progression and drug resistance.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): CLL is a malignancy of mature B cells characterized by clonal expansion of leukemic cells. Although less studied than AML and ALL, recent evidence suggests that m6A modifications also play a role in CLL development and progression.
Therapeutic Implications
Given the important role of m6A modifications in leukemia, targeting these modifications represents a promising therapeutic strategy. Small-molecule inhibitors of m6A writers and demethylases have shown efficacy in preclinical models of leukemia, particularly in reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis of leukemic cells.
Furthermore, understanding the mechanisms underlying m6A-mediated regulation of leukemic cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation can guide the development of more targeted and effective therapies.
Conclusions
m6A RNA modifications are key players in leukemia regulation, affecting various aspects of leukemic cell biology. Recent advances in understanding the mechanisms underlying m6A-mediated regulation of gene expression and leukemia development have opened new avenues for targeted interventions. As we continue to unravel the complexities of m6A modifications in leukemia, we can expect the development of more effective and personalized therapies for this devastating group of hematological malignancies.
Full text
The study was recently published in the Gene Expression.
Gene Expression (GE) is an open-access journal. It was launched in 1991 by Chicago Medical School Press, and transferred to Cognizant Communication Corporation in 1994. From August 2022, GE is published by Xia & He Publishing Inc.
GE publishes peer-reviewed and high-quality original articles, reviews, editorials, commentaries, and opinions on its primary research topics including cell biology, molecular biology, genes, and genetics, especially on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of human diseases.
GE has been indexed in Medline (1991-2021), Scopus, Biological Abstracts, Biosis Previews, ProQuest, etc.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Gene Expression
Article Title
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA Modification’s Regulatory Role in Acute and Chronic Leukemia
Article Publication Date
2-Aug-2024