Porous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of highly ordered, porous materials consisting of organic molecules that are linked by covalent bonds to form a network. They enable the construction of functional materials with molecular precision. Similar to metal organic frameworks (MOFs), which were discovered around 25 years ago and have already reached market maturity, COFs possess highly promising structural, optical and electronic properties for numerous applications, for example in gas and liquid storage, catalysis, sensor technology and energy applications.

Credit: Florian Auras
Porous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of highly ordered, porous materials consisting of organic molecules that are linked by covalent bonds to form a network. They enable the construction of functional materials with molecular precision. Similar to metal organic frameworks (MOFs), which were discovered around 25 years ago and have already reached market maturity, COFs possess highly promising structural, optical and electronic properties for numerous applications, for example in gas and liquid storage, catalysis, sensor technology and energy applications.
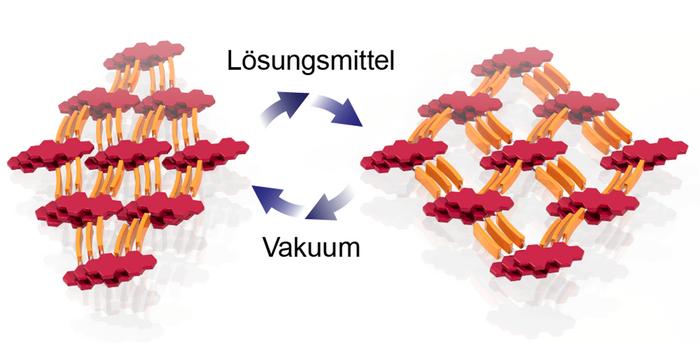
Previous research on COFs has generally focussed on the construction of rigid frameworks with static material properties. Dr Florian Auras and his team at the Chair of Molecular Functional Materials at TUD have now developed a design strategy for dynamic two-dimensional COFs that can open and close their pores in a controlled manner, similar to a sponge. “The main aim of the study was to equip these frameworks, which are normally very precisely ordered but rigid, with exactly the right degree of flexibility so that their structure can be switched from compact to porous. By adding solvent to the molecular sponge, we can now temporarily and reversibly change the local geometry as well as optical properties such as colour or fluorescence,” says Florian Auras, explaining his research approach.
The ability to switch the structural and optoelectronic properties of the materials back and forth in a targeted manner makes the materials particularly interesting for future applications in electronics and information technology. “Our research results form the basis for our further research into stimuli-responsive polymers, particularly with the aim of realising switchable quantum states. When working on COFs, I am always fascinated by how precisely their properties can be manipulated by controlling the molecular structure,” adds Auras.
Journal
Nature Chemistry
Article Title
Dynamic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks