A recent study spearheaded by Professor DANG Fei, alongside collaborators from Nanjing University, has unveiled a critical yet frequently neglected effect of microplastic pollution: its adverse influence on photosynthesis. This pivotal process serves as the backbone of Earth’s primary productivity and is paramount for maintaining global food security. Published in the esteemed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the research meticulously examines the interplay between microplastic exposure and its ramifications on photosynthetic processes across diverse ecosystems, including terrestrial, marine, and freshwater systems.
Microplastics, which are tiny plastic particles measuring less than 5 millimeters, have infiltrated ecosystems extending from the depths of the ocean’s trenches to the ice of polar glaciers. While there is a growing acknowledgment of the environmental crises surrounding plastic pollution, the specific effects of microplastics on the photosynthetic capabilities of various organisms remain poorly understood. A multitude of previous inquiries has produced fragmented or contradictory findings. These inconsistencies often arise from the complexities of ecosystems, the diverse types of affected autotrophic organisms, and the varying characteristics of microplastics themselves.
The ambiguity surrounding microplastic impacts on photosynthesis presents a significant hurdle to global initiatives aimed at achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Notable goals at risk include those focused on Zero Hunger, Good Health and Well-being, Responsible Consumption and Production, and Life Below Water. This study’s comprehensive analysis of over 3,200 records employs advanced meta-analysis and machine learning techniques to fill this knowledge gap.
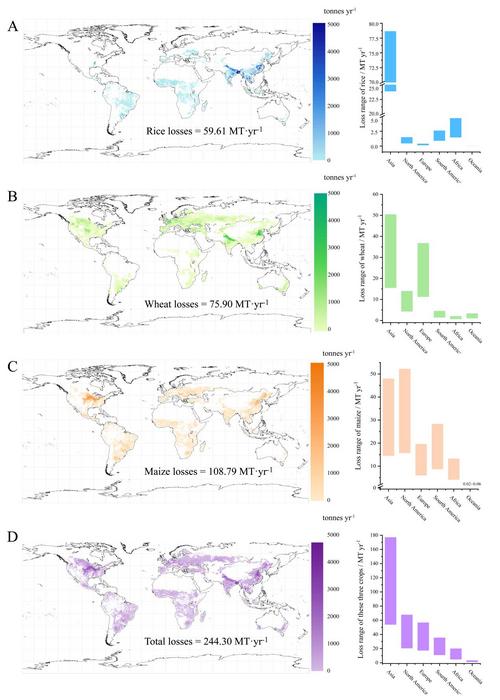
The results of the investigation demonstrate a concerning decline in photosynthetic efficiency in response to microplastic exposure. Specifically, the research indicates that microplastics reduce photosynthetic efficiency by approximately 7.05% to 12.12% among vital organisms such as terrestrial plants, marine macroalgae, and freshwater algae. When translated into numerical terms, these declines equate to an alarming estimated global loss of 4.11% to 13.52%, equivalent to 109.73 to 360.87 million tonnes per year, for essential staple crops like rice, wheat, and maize.
Beyond terrestrial implications, the study reveals that aquatic ecosystems are not spared from these detrimental effects. The inhibition of photosynthesis caused by microplastics is anticipated to result in substantial net primary productivity (NPP) losses ranging from 0.31% to 7.24%, equating to between 147.52 and 3,415.11 million tonnes of carbon per year. Such reductions in productivity foreshadow a potential decline in seafood production, estimated to be between 1.05 and 24.33 million tonnes annually. These findings illuminate the profound yet often invisible threat that microplastic pollution poses to global food supplies.
Yet, amid these grim findings, researchers highlight a potential avenue for remediation. The analysis suggests that a significant reduction—specifically a 13% decrease—in environmental microplastic levels could mitigate the losses in photosynthesis by approximately 30%. This reduction could stave off global losses ranging from 22.15 to 115.73 million tonnes per year in primary crops and an estimated 0.32 to 7.39 million tonnes annually in seafood production.
The research urges immediate action to address microplastic pollution as a critical factor influencing global primary productivity. It underscores the need to incorporate viable strategies for plastic pollution mitigation into comprehensive sustainability and food security frameworks. Additionally, the researchers advocate for enhanced data collection and transparency regarding the scope and mechanisms by which microplastics disrupt photosynthetic processes in future field research.
As emerging technologies in remote sensing and data science evolve, the capacity for researchers to gain more precise insights into this emerging threat will likely expand. Greater availability of high-quality field data is crucial, contributing to a more refined understanding of microplastics’ ecological footprints. Such insights will play an essential role in guiding international treaty negotiations regarding plastic pollution and support initiatives aimed at fulfilling the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
In light of these pressing issues, the scientific community is called upon to present a united front in advancing research and public awareness surrounding microplastic pollution. Dismantling the knowledge gaps will not only aid policymakers but will also empower society to take informed action against the plastic crisis. A concerted effort is required to pivot from awareness to actionable change, ensuring a sustainable future for the planet’s ecosystems and food security.
Understanding the mechanisms through which microplastics affect photosynthesis is imperative. Future studies should further explore the direct interactions between microplastics and the cellular structures of photosynthetic organisms, focusing on how these tiny pollutants disrupt biochemical pathways and physiological processes. Additionally, long-term ecological studies will be pivotal in assessing the cumulative effects of microplastics on ecosystem health and resilience.
With the ongoing rise in environmental degradation, it is paramount that stakeholders across various sectors recognize and act upon the urgent need to confront microplastic pollution. Everyone, from policymakers to consumers, must engage in reducing plastic use and fostering sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts will be necessary to mitigate the impacts highlighted by the research and preserve the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
Given the complexity of ecosystem interactions, interdisciplinary approaches combining biology, ecology, environmental science, and policy-making will enhance our understanding of microplastic pollution and its effects. The knowledge gained could play a crucial role in shaping legislative frameworks and public outreach campaigns to combat pollution effectively.
In conclusion, the study conducted by Prof. DANG Fei and his team not only highlights a vital environmental issue but also serves as a clarion call for immediate action. The intricate connections between microplastic pollution, photosynthesis, and food security must be addressed with urgency. By fostering a culture of sustainability and responsible resource management, we can safeguard our planet’s future and ensure that ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.
Subject of Research: Effects of microplastic pollution on photosynthesis
Article Title: A global estimate of multiecosystem photosynthesis losses under microplastic pollution
News Publication Date: 10-Mar-2025
Web References: DOI
References: N/A
Image Credits: Credit: DANG Fei
Keywords: Microplastic pollution, photosynthesis, food security, environmental sustainability, primary productivity.