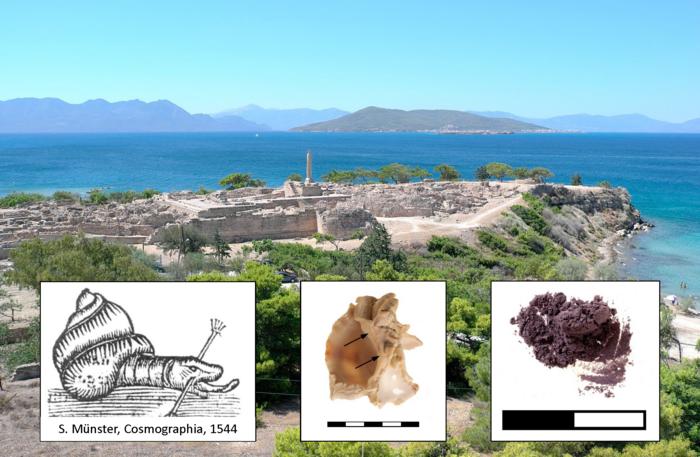
The Greek island of Aegina was home to a Late Bronze Age purple dye workshop, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lydia Berger of Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, Austria and colleagues.

Credit: Aegina Kolonna excavation, Department of Classics, Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, CC-BY 4.0 (
The Greek island of Aegina was home to a Late Bronze Age purple dye workshop, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lydia Berger of Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, Austria and colleagues.
Colored dyes were a significant commodity in the Mediterranean region during the Late Bronze Age, and understanding the production of these dyes is valuable for interpretations of culture and trade at the time. In this study, Berger and colleagues describe the site of a purple dye workshop from the 16th century BC located at Aegina Kolonna in the Saronic Gulf.
The presence of a dye workshop at this site is inferred from three main lines of evidence: purple pigment preserved on ceramic fragments, which are likely remnants of dye containers; dyeing tools, including grinding stones and a waste pit; and crushed shells of marine snails whose bodies are harvested for these pigments. Analysis of the shells and the chemical composition of the pigments indicate that the workshop predominantly used one species of Mediterranean snail, the banded dye-murex.
Excavation at this site also uncovered many burnt bones from young mammals, mainly piglets and lambs. The authors hypothesize that these could be the remains of animals ritually sacrificed as spiritual offerings to protect the site of production, a practice known from other cultural sites, although the exact connection between these bones and the dye production is not yet fully clear.
This site provides valuable insights into the tools and processes of Mycenaean purple dye production. Further research might reveal more information about the scale of dye production at Kolonna Aegina, the details of the on-site procedures, and the use of this dye in regional trade.
The authors add: “For the first time, the discovery of remarkable quantities of well-preserved pigment, together with a large number of crushed mollusk shells and a few functional facilities, allow a detailed insight into the production of purple-dye on the Greek island of Aegina around 3600 years ago. Chemical analysis by HPLC, malacological, zoological, and archaeological studies illustrate the technical process and peculiarities of early dye production and prove a workshop within the Late Bronze Age settlement.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE:
Citation: Berger L, Forstenpointner G, Frühauf P, Kanz F (2024) More than just a color: Archaeological, analytical, and procedural aspects of Late Bronze Age purple-dye production at Cape Kolonna, Aegina. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0304340.
Author Countries: Austria
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Journal
PLoS ONE
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
More than just a color: Archaeological, analytical, and procedural aspects of Late Bronze Age purple-dye production at Cape Kolonna, Aegina
Article Publication Date
12-Jun-2024
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.