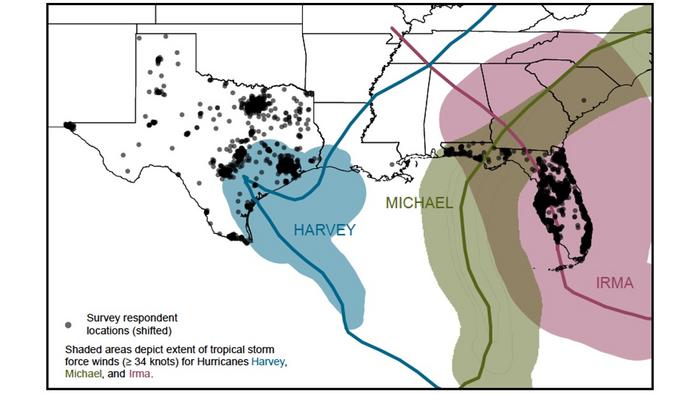
Rapid climate change is prompting adaptation to threats such as tropical cyclones, wildfires, and droughts—but relatively trivial adaptation actions may lull people into inaccurate perceptions of their personal risk. Researchers from the University of California, Irvine; Stanford University; and the University of California, Los Angeles surveyed 2,774 Texas and Florida residents about tropical cyclones—also known in North America as hurricanes—five times between 2017 and 2022. The survey window included three major landfalling tropical cyclones: Hurricanes Harvey (2017), Irma (2017), and Michael (2018). Participants were recruited through the probability-based online panel KnowledgePanel and asked about their perceived risk from tropical cyclones, as well as adaptation activities, including assembling an emergency supply kit, installing hurricane shutters, developing and practicing an emergency plan, and purchasing flood insurance. Gabrielle Wong-Parodi and colleagues found that perception of personal risk, including the likelihood of injury and home damage, declined as time passed after hurricanes. On average, personal tropical cyclone risk perceptions were positively associated with adaptation actions. However, adapters also showed declining risk perception over time. Yet, the authors note that climate change is making tropical cyclones more intense over time— and adaptation activities cannot reduce overall risk of event occurrence. According to the authors, these activities may counterintuitively lower personal risk perceptions and subsequent adaptation behaviors, paradoxically leaving people less prepared for future climate threats. The authors contend that policies and programs supporting sustainment of long-term proactive adaptations are warranted, especially among those who may have fewer resources.

Credit: Nina Berlin Rubin
Rapid climate change is prompting adaptation to threats such as tropical cyclones, wildfires, and droughts—but relatively trivial adaptation actions may lull people into inaccurate perceptions of their personal risk. Researchers from the University of California, Irvine; Stanford University; and the University of California, Los Angeles surveyed 2,774 Texas and Florida residents about tropical cyclones—also known in North America as hurricanes—five times between 2017 and 2022. The survey window included three major landfalling tropical cyclones: Hurricanes Harvey (2017), Irma (2017), and Michael (2018). Participants were recruited through the probability-based online panel KnowledgePanel and asked about their perceived risk from tropical cyclones, as well as adaptation activities, including assembling an emergency supply kit, installing hurricane shutters, developing and practicing an emergency plan, and purchasing flood insurance. Gabrielle Wong-Parodi and colleagues found that perception of personal risk, including the likelihood of injury and home damage, declined as time passed after hurricanes. On average, personal tropical cyclone risk perceptions were positively associated with adaptation actions. However, adapters also showed declining risk perception over time. Yet, the authors note that climate change is making tropical cyclones more intense over time— and adaptation activities cannot reduce overall risk of event occurrence. According to the authors, these activities may counterintuitively lower personal risk perceptions and subsequent adaptation behaviors, paradoxically leaving people less prepared for future climate threats. The authors contend that policies and programs supporting sustainment of long-term proactive adaptations are warranted, especially among those who may have fewer resources.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
A longitudinal investigation of risk perceptions and adaptation behavior in the US Gulf Coast
Article Publication Date
9-Apr-2024