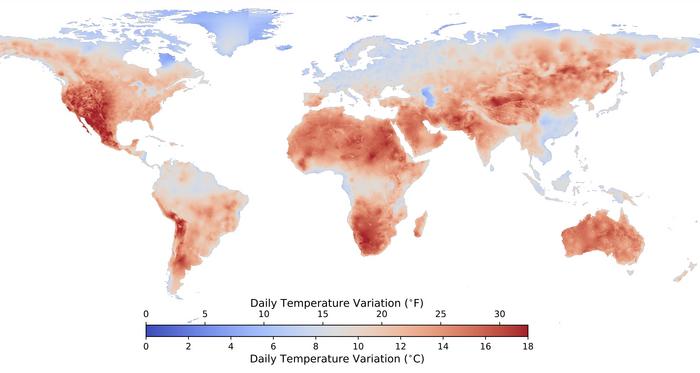
Extreme heat can harm human health, but so can temperature extreme swings. Large daily temperature variation (DTV) has been associated with elevated mortality in studies around the world. Trees and other vegetation can lower DTV, as trees reduce temperature through transpiration during the day and also trap long-wave radiation in the atmosphere under the canopy at night, increasing temperature. But green space is not equally distributed in most cities. Shengjie Liu and Emily Smith-Greenaway examined inequality in DTV exposure in the US, using monthly nighttime and daytime land surface temperature data from satellites. The authors find that exposure to large DTV differs significantly between White and non-White populations at the census tract level. Specifically, the authors note larger DTV exposure among Black and Hispanic populations, who experience temperature swings of up to 3 degrees Celsius larger than White census tracts. Unequal exposure to DTV is also observed between low-income and high-income populations, though to a lesser degree. The differences in DTV seem to be driven by green space in the urban environment, although the inequalities in this case are larger than the inequalities in experiencing the urban heat island effect, a more well-known consequence of the different urban fabrics that comprise different American neighborhoods. According to the authors, DTV should be considered a fundamental source of climate-induced health disparities.

Credit: Liu & Smith-Greenaway
Extreme heat can harm human health, but so can temperature extreme swings. Large daily temperature variation (DTV) has been associated with elevated mortality in studies around the world. Trees and other vegetation can lower DTV, as trees reduce temperature through transpiration during the day and also trap long-wave radiation in the atmosphere under the canopy at night, increasing temperature. But green space is not equally distributed in most cities. Shengjie Liu and Emily Smith-Greenaway examined inequality in DTV exposure in the US, using monthly nighttime and daytime land surface temperature data from satellites. The authors find that exposure to large DTV differs significantly between White and non-White populations at the census tract level. Specifically, the authors note larger DTV exposure among Black and Hispanic populations, who experience temperature swings of up to 3 degrees Celsius larger than White census tracts. Unequal exposure to DTV is also observed between low-income and high-income populations, though to a lesser degree. The differences in DTV seem to be driven by green space in the urban environment, although the inequalities in this case are larger than the inequalities in experiencing the urban heat island effect, a more well-known consequence of the different urban fabrics that comprise different American neighborhoods. According to the authors, DTV should be considered a fundamental source of climate-induced health disparities.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Racial and ethnic minorities disproportionately exposed to extreme daily temperature variation in the United States
Article Publication Date
21-May-2024