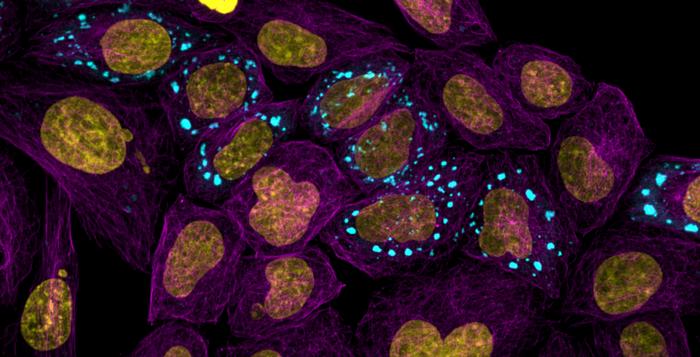
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed an atlas of proteins describing how they behave inside human cells. This tool could be used to search for the origins of diseases which are related to proteins misbehaving such as dementia and many cancers.

Credit: Andrew Seeber
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed an atlas of proteins describing how they behave inside human cells. This tool could be used to search for the origins of diseases which are related to proteins misbehaving such as dementia and many cancers.
The atlas, which is published in Nature Communications, has allowed the researchers to find new proteins inside cells that are responsible for a range of important bodily functions. The team focuses on a droplet-like part of the cell called a condensate which is a meeting hub for proteins to go and organise themselves. These hubs are also key sites where disease processes start.
The predictions are available with the paper so researchers around the globe can explore their protein targets of interest and any surrounding condensate systems.
“This model has allowed us to discover new components in membraneless compartments in biology as well as discover new principles underlying their function.” said Professor Tuomas Knowles, who led this research.
Protein condensates
Cells are made of carefully organised molecules and one method they use to organise themselves is by meeting inside a condensate. This hub is microscopic and found inside a cell. These condensates are part of the essential machinery that makes living cells work.
“To date we have not had a comprehensive map of which proteins go together into which condensates, but in our work we provide a first such atlas,” said Knowles.
Using AI
The rules directing proteins inside cells are not completely understood so the team decided to build this atlas to predict which proteins meet inside condensates.
“What motivated this research was the desire to understand the full complexity of protein condensates and to go a layer deeper than what scientists have researched so far,” said Dr Kadi Liis Saar, first author on this research and a postdoctoral fellow at the Centre for Misfolding Diseases.
The researchers used large databases, such as StringDB and BioGRID, which contain data on many aspects of cells, along with more in-depth case studies about individual condensates.
The power of AI lets scientists combine these data even though the information is complex, vast, and difficult to compare. Where previous work focussed on a handful of proteins, the atlas can characterise the full landscape of a cell.
“With this atlas we can make predictions about every single protein in a cell, where exactly it would be found and what sorts of other proteins it interacts with,” commented Saar. “We hope that this generates opportunities for researchers and opens up new possibilities for intervention in diseases associated with aberrant condensate formation.”
Protein discoveries
The AI found proteins present in the model cell that had never been observed before. If these proteins are now found in a lab then this is a good indicator that the AI is accurate.
“In our study, we discovered proteins within condensates that have never been seen there before. These proteins are involved in important functions in the body, such as the distribution of fat, the creation of actin inside cells, and the creation of new proteins. These proteins were not detected in the previous study that we used as our training set.
“We hope these data will enable new discoveries about the biological roles of condensates as well as the biophysical drivers behind condensate formation.”
Journal
Nature Communications
Article Title
Protein Condensate Atlas from predictive models of heteromolecular condensate composition
Article Publication Date
10-Jul-2024