Credit: GREEN ENERGY AND INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION
Urban Air Mobility refers to the use of Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft to transport people and goods across urban areas, potentially easing the notorious ground traffic congestion. As cities worldwide grapple with transportation inefficiencies, Chengdu’s initiative could serve as a blueprint for sustainable urban transit.
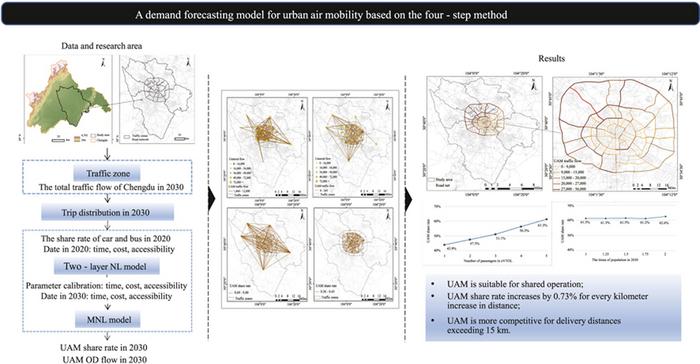
The study utilized a four-step forecasting method that includes trip generation, distribution, modal split, and traffic assignment to predict UAM demand. The researchers combined a nested logit (NL) model with a multinomial logit (MNL) model, overcoming the absence of historical UAM data to estimate future share rates effectively.
Key findings suggest that UAM will become a more competitive mode of transport as the travel distance increases, particularly surpassing 15 kilometers. This is due to eVTOLs’ ability to bypass traditional road traffic, significantly reducing travel time. The data indicates that for every additional kilometer, the UAM share rate could increase by 0.73%, making it a viable option for medium to long-range urban transport.
The study also highlights the importance of shared operation models for UAM. By fully implementing shared operations, where eVTOLs carry multiple passengers per trip, the UAM share rate could see a significant boost, making it an economically viable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional road transport.
Furthermore, the research pinpoints routes within Chengdu that could benefit most from UAM, suggesting that prioritizing these routes could facilitate efficient UAM integration into the existing urban transport network. These routes predominantly cover areas with high traffic volumes and are expected to alleviate congestion significantly.
Despite its promising outlook, the integration of UAM in Chengdu faces several challenges. The success of this futuristic transportation hinges on several factors including technological advancements, regulatory approvals, public acceptance, and infrastructural developments. As UAM is still in its nascent stages globally, continuous research and adaptive strategies will be essential to its success.
The implications of this study extend beyond traffic management; they encompass economic benefits through job creation in the UAM sector and significant reductions in urban carbon emissions. As Chengdu aims to position itself at the forefront of urban transport innovation, the global community watches closely, potentially looking to replicate this model in other megacities facing similar urban mobility challenges.
This pioneering research not only maps out a feasible pathway for Chengdu’s UAM adoption but also sets a benchmark for other cities aiming to integrate similar technologies into their urban landscapes. As we move towards more sustainable urban environments, Chengdu’s journey may well be a glimpse into the future of urban mobility.
###
Reference
Authors: Wenqiu Qu a b, Jie Huang b c, Chenglong Li d, Xiaohan Liao a b e
Affiliations:
aState Key Laboratory of Resources and Environment Information System, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
bCollege of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
cKey Laboratory of Regional Sustainable Development Modeling, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
dCivil Aviation Flight University of China, Guanghan, 618307, China
eThe Research Center for UAV Applications and Regulation, CAS, Beijing 100101, China
Title of original paper: A demand forecasting model for urban air mobility in Chengdu, China
Article link:
Journal: Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation
DOI: 10.1016/j.geits.2024.100173
Journal
Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation