Hepatocellular Carcinoma and the Expanding Role of Liver Transplantation: A Comprehensive Update
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) stands as the predominant form of primary liver cancer worldwide, accounting for the lion’s share of liver cancer-related mortality. As the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, HCC presents a daunting challenge to clinicians and researchers alike. Over recent years, significant advancements have been made in the understanding of HCC’s pathophysiology, patient selection for liver transplantation (LT), and the management of those awaiting transplant. This review delves into the current landscape of HCC treatment, emphasizing the evolving criteria for liver transplantation and the crucial role of bridging and downstaging therapies designed to optimize patient outcomes.
Epidemiological shifts have marked the incidence of HCC in recent decades. Historically dominated by viral hepatitis B and C infections, the etiological profile is now increasingly complicated by metabolic-associated steatohepatitis (MASH/MASLD) and alcohol-related liver disease. These conditions catalyze the development of chronic liver injury and cirrhosis, forming a fertile ground for hepatocarcinogenesis. The incidence of HCC is notably higher in men and shows considerable geographic variability, with East Asia bearing a disproportionate burden. This regional predilection underscores the importance of tailoring surveillance and treatment programs to specific patient populations and risk factors.
A critical element in improving survival outcomes is the early detection of HCC, as the tumor’s asymptomatic nature in early stages delays diagnosis until advanced disease has developed. Standard surveillance protocols recommend biannual ultrasound combined with serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) testing in high-risk populations, such as patients with cirrhosis. However, these methods suffer from limited sensitivity and specificity, particularly in obese patients or those with nodular liver parenchyma. To overcome these challenges, advanced imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans are increasingly employed to enhance diagnostic accuracy and guide clinical decision-making.
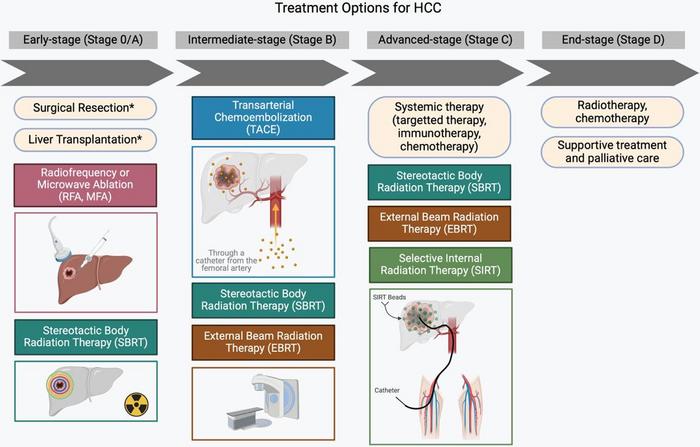
Staging systems form a cornerstone in evaluating HCC patients for appropriate therapeutic interventions. Among them, the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) system remains the most widely employed, integrating tumor burden, liver function parameters, and performance status into a unified framework. Within this system, liver transplantation occupies a central role as the most definitive treatment, capable of eliminating both the tumor and the underlying cirrhotic milieu that fosters carcinogenesis. The Milan Criteria have long served as the benchmark for LT eligibility, restricting candidates to a single tumor ≤5 cm or up to three tumors each ≤3 cm without vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread. Nonetheless, evolving data have prompted exploration of expanded criteria to include patients with more extensive disease without compromising post-transplant survival.
Due to stringent LT eligibility standards and limited availability of donor organs, alternative strategies to maintain transplant candidacy have become indispensable. Bridging therapies, chiefly locoregional treatments such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), are utilized to prevent tumor progression in patients facing prolonged wait times for transplantation. These interventions not only halt growth but in some cases induce tumor necrosis, enhancing the likelihood of successful transplantation outcomes. Guidelines particularly advocate bridging for University of Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) Stage T2 lesions when anticipated wait times exceed six months, highlighting the balance clinicians must strike between disease control and transplant timing.
Complementing bridging approaches, downstaging therapies seek to reduce tumor burden in patients initially outside transplant criteria, rendering them eligible candidates. TACE remains the primary modality employed in downstaging, often combined with systemic therapies such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) or emerging immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). These systemic agents have transformed the therapeutic landscape of advanced HCC by modulating tumor biology and the host immune environment. While originally reserved for non-transplant candidates, integration of TKIs and ICIs into pre-transplant treatment regimens shows promise in expanding the LT pool and improving post-transplant survival.
Liver transplantation confers a potential cure by removing both malignant tissue and cirrhotic liver architecture, yet the specter of HCC recurrence after LT remains a formidable clinical challenge. Recurrence risks are influenced by factors such as tumor differentiation, vascular invasion, and AFP levels at transplant. Advances in selection criteria have incorporated these biological markers to better stratify recurrence risk and guide transplant decisions. Despite these refinements, ongoing surveillance post-transplant is crucial. Imaging and AFP monitoring are standard practices for early detection of recurrence, which may entail aggressive interventions including surgical resection or systemic therapies to optimize patient survival.
The integration of systemic therapies into HCC management has revolutionized treatment paradigms, especially for advanced or recurrent disease. ICIs, targeting immune pathways that tumors exploit to evade immune surveillance, demonstrate durable responses and synergize with locoregional therapies in select patient subsets. Meanwhile, TKIs such as sorafenib and lenvatinib continue to form the backbone of systemic treatment, inhibiting angiogenesis and tumor proliferation signaling pathways. The evolving interplay between these systemic agents and transplant candidacy is a fertile area of research, with the goal of enhancing tumor control and expanding transplant eligibility.
Despite the advancements, the limited donor organ pool remains a critical bottleneck in LT for HCC. The need for rigorous patient selection is emphasized to optimize organ allocation, balancing tumor biology and transplant outcomes. Novel predictive models incorporating genetic and molecular tumor profiling are under investigation to refine eligibility criteria further and personalize treatment strategies. Parallel efforts focus on improving early detection technologies and refining downstaging protocols to maximize the number of patients benefiting from LT.
In conclusion, liver transplantation retains its status as a curative option for HCC patients who meet specific clinical and tumor-related criteria. Bridging and downstaging therapies play pivotal roles in managing patients awaiting transplantation or those initially deemed ineligible. Advances in systemic treatments offer new avenues to control disease progression and expand transplant candidacy. Looking forward, ongoing research aims to optimize selection protocols, enhance surveillance techniques, and integrate multidisciplinary approaches to reduce recurrence and improve long-term survival. The complex interplay of tumor biology, liver function, and immunological interventions continues to define the evolving role of liver transplantation in the fight against hepatocellular carcinoma.
Subject of Research: Hepatocellular carcinoma and liver transplantation treatment strategies
Article Title: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and the Role of Liver Transplantation: An Update and Review
News Publication Date: 24-Feb-2025
Web References: https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2024.00432
Image Credits: Ahmet Gurakar, Lynette M. Sequeira