RNA has long been considered only as a passive messenger in the cell, produced by DNA transcription to transfer genetic information to the protein factories, the ribosomes. However, it has turned out, that RNA does much more than that. In addition to the coding DNA just described, there is also non-coding DNA controlling many cellular processes by regulating the activity of genes at many levels. No less than a dozen RNA classes have been identified nowadays. RNAi for example, is used by the cell to degrade particular RNA targets to silence genes, when it comes to fighting foreign viral DNA.

Credit: MPI of Molecular Physiology
RNA has long been considered only as a passive messenger in the cell, produced by DNA transcription to transfer genetic information to the protein factories, the ribosomes. However, it has turned out, that RNA does much more than that. In addition to the coding DNA just described, there is also non-coding DNA controlling many cellular processes by regulating the activity of genes at many levels. No less than a dozen RNA classes have been identified nowadays. RNAi for example, is used by the cell to degrade particular RNA targets to silence genes, when it comes to fighting foreign viral DNA.
Readers, writers, and erasers
RNA interacts with a plethora of biomolecules, not only other RNAs or DNA but also proteins and metabolites. The resulting regulatory complexes control diverse vital cellular processes and errors can cause diseases. RNA’s fate is determined by chemical modifications that affect its stability, structure and interactions and thereby its fate. More than 170 distinct RNA modifications have been described so far. The most abundant is the methylation on the N6-position of the RNA-nucleotide adenosine (m6A). It allows the cell to quickly respond to environmental changes by initiating appropriate cellular responses, such as division, differentiation or migration. This is why RNA-methylation needs to be tightly controlled, taken care of by a set of proteins: “writers” deposit, “readers” recognize and “erasers” remove the methyl group.
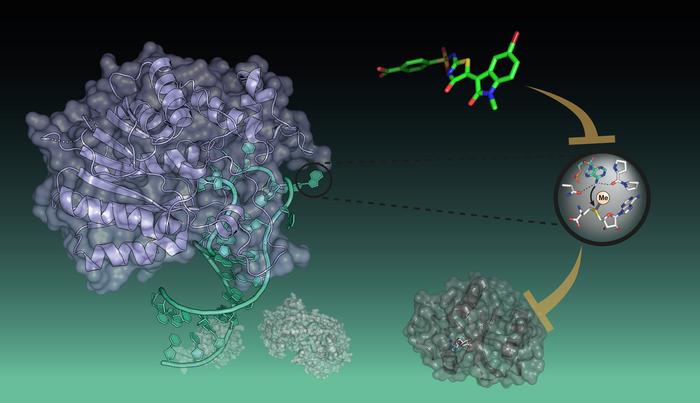
New substance prevents writing to RNA
Aberrant RNA methylation has been associated with cancers and other human diseases, making “writers” an attractive therapeutic target. Only a handful of RNA m6A writers have been identified so far. And only for one of them, METTL3, potent inhibitors have been reported. These molecules prevent the writer from absorbing the ink, the biomolecule S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). The group of Peng Wu has now identified the first inhibitor of the writer METTL16. However, in contrast to the before-mentioned inhibitors, it showed a different mode of action: it prevents the interaction of METTL16 with RNA. The scientists were able to identify this new type of inhibitor by developing an assay evaluating the disruption between METTL16 and a fluorophore-labeled mRNA substrate.
“Certain cancer cells have elevated writer levels and are also more vulnerable to reduction of SAM levels, which makes them promising anticancer targets. However, the exact biological consequences of METTL16’s binding to RNA substrates are not yet clearly determined. With our work, we lay the foundation for a better investigation of the role of METTL16 in disease and health, but also for the development of novel RNA-targeting therapeutics”, says Peng Wu.
Journal
JACS Au
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Aminothiazolone Inhibitors Disrupt the Protein–RNA Interaction of METTL16 and Modulate the m6A RNA Modification
Article Publication Date
21-Mar-2024