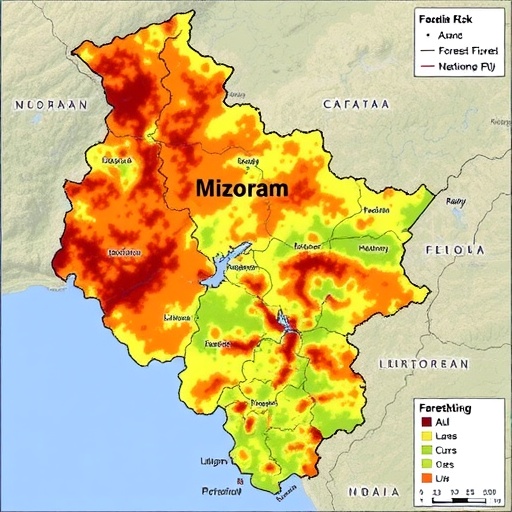
In a recent publication, Gupta, Shukla, and Shukla have put forth answers to critical commentary on their pioneering work regarding machine learning-based forest fire susceptibility mapping in Southern Mizoram, an essential area within the Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot. This region is characterized by its rich biological diversity and geological significance, but it also faces increasing threats from climate change and human activities. The researchers argue that their machine learning framework not only provides an innovative analytical tool for assessing forest fire risks but also serves as a crucial step in conservation efforts aimed at preserving the unique ecological attributes of this biodiversity hotspot.
The authors highlight that their initial study was groundbreaking in utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze historical fire occurrence data, topographical features, and vegetation types in Southern Mizoram. This approach allowed them to create a susceptibility map, effectively identifying regions that are at a higher risk of forest fires. Such predictive capabilities are invaluable, particularly as climate change continues to alter weather patterns, leading to a higher frequency of extreme weather events. This increased fire susceptibility poses a significant challenge to biodiversity conservation efforts in the region.
In their response to comments, Gupta et al. concisely address various critiques regarding the methodology employed in their research. They clarify that the machine learning techniques used were not only robust but also appropriate for the dataset and the specific ecological context. By employing decision trees and ensemble methods, the researchers minimized biases that could arise from traditional fire risk assessments, showcasing the power of data-driven models in ecological studies.
The significance of their mapping efforts transcends academic interest, influencing practical conservation strategies and policy decisions. By providing local stakeholders and policymakers with actionable insights, the research fosters a proactive stance towards forest fire management in Southern Mizoram. These maps serve as a vital tool in prioritizing resource allocation for firefighting efforts, informing land use planning, and implementing preemptive measures to protect vulnerable ecosystems.
Addressing the score of misinformation surrounding machine learning applications in ecology, Gupta’s team emphasizes transparency in their modeling process. They detail the importance of data quality and the need for continuous validation of predictions through field observations. This attention to detail reinforces the credibility of their results, instilling confidence in both scientific peers and local communities who stand to benefit from the research.
Moreover, the response sheds light on the interplay between machine learning techniques and traditional ecological knowledge. Gupta and colleagues posit that integrating local wisdom with advanced scientific tools can enhance the predictive power of fire susceptibility mapping. By combining empirical knowledge regarding local flora and fauna with machine-driven analytics, a more holistic understanding of fire dynamics emerges, ultimately leading to more effective ecological management practices.
The researchers also acknowledge the challenges associated with data availability and the need for enhanced coordination among research institutions, government bodies, and NGOs to develop comprehensive datasets. They advocate for the establishment of collaborative platforms that facilitate data sharing, thereby laying the groundwork for future studies that further refine forest fire susceptibility models.
As the discourse surrounding their research continues, Gupta et al. remain steadfast in their belief that embracing innovative technologies like machine learning can significantly contribute to biodiversity conservation. They argue that the results from their study not only provide immediate implications for fire risk management but also pave the way for long-term ecological resilience.
In conclusion, the work of Gupta, Shukla, and Shukla stands as a testament to the potential of synergizing cutting-edge technology with environmental science. Their proactive approach to using machine learning for mapping forest fire susceptibility offers a valuable resource for understanding and mitigating the risks faced by Southern Mizoram’s unique ecosystems. As academic discussions progress, it remains essential to emphasize the importance of this intersection, as it may well determine the future of conservation efforts in biodiversity hotspots around the globe.
Further exploration into the relationship between fire ecology and machine learning could yield invaluable insights, guiding research endeavors in other vulnerable regions. The researchers invite other scientists to build on their work, expanding the understanding of fire dynamics in conjunction with climate change impacts, which emphasize the necessity for ongoing dialogue in the environmental science community.
Ultimately, the rigorous debate surrounding their findings and the subsequent response reflects the vibrant nature of scientific inquiry, where questions and critiques lead to greater clarity and understanding. As we move forward in an era characterized by rapid environmental changes, the marriage of machine learning and ecological studies may herald a new age of informed decision-making in natural resource management.
Subject of Research: Forest fire susceptibility mapping using machine learning methods in Southern Mizoram.
Article Title: Answer to “Comments on Machine learning-based forest fire susceptibility mapping of Southern Mizoram, a part of Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot”.
Article References:
Gupta, P., Shukla, A.K. & Shukla, D.P. Answer to “Comments on Machine learning-based forest fire susceptibility mapping of Southern Mizoram, a part of Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot”.
Environ Sci Pollut Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-025-36831-4
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: Machine learning, forest fire, susceptibility mapping, Southern Mizoram, Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot, ecological conservation, climate change, predictive modeling.