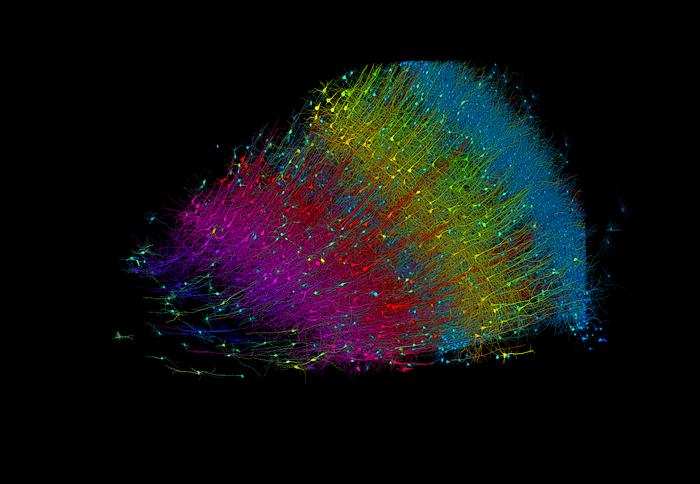
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue may not sound like much. But considering that tiny square contains 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, all amounting to 1,400 terabytes of data, Harvard and Google researchers have just accomplished something enormous.

Credit: Google Research and Lichtman Lab
A cubic millimeter of brain tissue may not sound like much. But considering that tiny square contains 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, all amounting to 1,400 terabytes of data, Harvard and Google researchers have just accomplished something enormous.
A Harvard team led by Jeff Lichtman, the Jeremy R. Knowles Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and newly appointed dean of science, has co-created with Google researchers the largest synaptic-resolution, 3D reconstruction of a piece of human brain to date, showing in vivid detail each cell and its web of neural connections in a piece of human temporal cortex about half the size of a rice grain.
The feat, published in Science, is the latest in a nearly 10-year collaboration with scientists at Google Research, who combine Lichtman’s electron microscopy imaging with AI algorithms to color-code and reconstruct the extremely complex wiring of mammal brains. The paper’s three co-first authors are former Harvard postdoctoral researcher Alexander Shapson-Coe; Michał Januszewski of Google Research, and Harvard postdoctoral researcher Daniel Berger.
The collaboration’s ultimate goal, supported by the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative, is to create a high-resolution map of a whole mouse brain’s neural wiring, which would entail about 1,000 times the amount of data they just produced from the 1-cubic-millimeter fragment of human cortex.
“The word ‘fragment’ is ironic,” Lichtman said. “A terabyte is, for most people, gigantic, yet a fragment of a human brain – just a miniscule, teeny-weeny little bit of human brain – is still thousands of terabytes.”
The latest map in Science contains never-before-seen details of brain structure, including a rare but powerful set of axons connected by up to 50 synapses. The team also noted oddities in the tissue, such as a small number of axons that formed extensive whorls. Since their sample was taken from a patient with epilepsy, they’re unsure if such unusual formations are pathological or simply rare.
Lichtman’s field is “connectomics,” which, analogous to genomics, seeks to create comprehensive catalogues of brain structure, down to individual cells and wiring. Such completed maps would light the way toward new insights into brain function and disease, about which scientists still know very little.
Google’s state-of-the-art AI algorithms allow for reconstruction and mapping of brain tissue in three dimensions. The team has also developed a suite of publicly available tools researchers can use to examine and annotate the connectome.
“Given the enormous investment put into this project, it was important to present the results in a way that anybody else can now go and benefit from them,” said Google Research collaborator Viren Jain.
Next the team will tackle the mouse hippocampal formation, which is important to neuroscience for its role in memory and neurological disease.
Journal
Science
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
A petavoxel fragment of human cerebral cortex reconstructed at nanoscale resolution
Article Publication Date
10-May-2024