In a recently conducted modeling study published in JAMA Network Open, researchers have provided a nuanced economic analysis of COVID-19 vaccination across different age groups within the United States population. This investigation brings to light the divergent cost-effectiveness profiles of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines when stratified by age, a critical factor influencing public health vaccination strategies in an ever-evolving pandemic landscape. The work further underscores the importance of revisiting economic evaluations in the context of emerging real-world evidence and shifting disease burden.
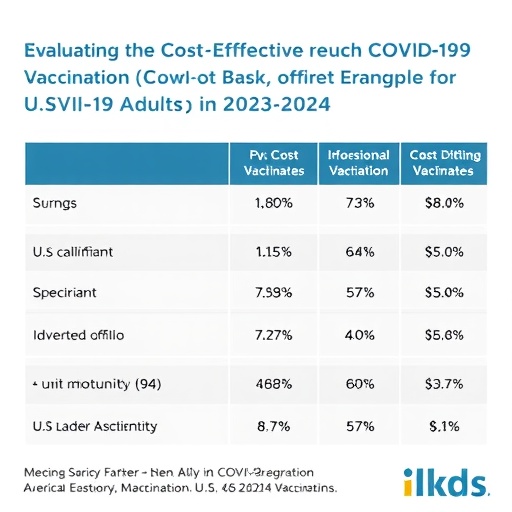
The study employs sophisticated computational modeling techniques to simulate vaccination outcomes, factoring in parameters such as vaccine efficacy, disease incidence, healthcare resource utilization, and broader demographic variables. By segmenting the population into three age brackets—presumably young people, adults, and older adults—the research delineates the varying degrees of economic favorability that vaccinations offer across the lifespan. Intriguingly, the model reveals that older age groups consistently benefit from vaccination, demonstrating favorable and generally stable cost-effectiveness despite fluctuations in key input parameters.
Conversely, the youngest adult group exhibits a more volatile response to changes in modeled parameters. These variations suggest a sensitivity that might be attributable to lower absolute risk of severe disease or to differences in behavioral and epidemiological factors influencing transmission and vaccine uptake. This complexity likely necessitates more targeted analytical refinement and the potential integration of additional variables such as long COVID incidence or indirect economic impacts in future modeling iterations.
The researchers emphasize that as the epidemiological landscape of COVID-19 continues to change—driven by factors like emerging variants, booster uptake trends, and shifting immunity profiles—the existing economic assessments must be dynamically updated. This adaptive approach ensures that public health policy, especially immunization recommendations, remains grounded in the most current and comprehensive evidence. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) has taken these findings into serious consideration in formulating their guidance for the 2023 to 2024 COVID-19 mRNA vaccination campaigns.
From a methodological standpoint, the modeling framework integrates demographic data, cost parameters, and vaccine efficacy data sourced from clinical trials and surveillance to project economic outcomes over time. This blend of clinical and economic inputs enables multifaceted decision-making that weighs not only health benefits but also financial sustainability and resource allocation within healthcare systems. Such modeling studies serve as indispensable tools for policymakers tasked with optimizing vaccine deployment amid constrained budgets and competing public health priorities.
One of the compelling aspects of this study is the granular approach to economic favorability that transcends simplistic age categorization. By systematically analyzing the cost-effectiveness ratios across age-defined cohorts, the study identifies critical thresholds where vaccination campaigns produce the highest returns in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and healthcare cost savings. This stratification aids in targeting interventions and tailoring communication strategies that could enhance vaccine acceptance among demographically distinct groups.
In terms of public health implications, the robust evidence supporting vaccination in older adults reinforces the urgency of maintaining high immunization coverage in vulnerable populations. The stability of cost-effectiveness in these groups, despite uncertainties in parameter inputs, provides a scientifically sound rationale for prioritizing boosters and vaccine access for seniors. Furthermore, insights regarding the sensitivity observed in younger populations highlight opportunities for refining vaccination strategies, potentially incorporating behavioral factors or alternative dosing schedules to maximize benefits.
Another critical dimension addressed by this modeling study is the interplay between direct health outcomes and economic consequences. Vaccination reduces the incidence of severe COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization and extensive medical intervention, resulting in tangible cost savings. Moreover, vaccination may mitigate broader societal costs, including productivity losses and long-term disability, though these factors are often challenging to quantify precisely in modeling frameworks and may warrant future incorporation.
This research also underscores the dynamic nature of health economic evaluations during ongoing pandemics, where rapidly changing variables, such as viral transmissibility and vaccine escape potential, challenge static models. The authors advocate for continuous data integration from emerging clinical and epidemiological studies to recalibrate models, thereby enhancing the precision of cost-effectiveness predictions and ensuring relevance to current public health realities.
Moreover, the findings could have sweeping implications beyond the United States, informing global vaccination policies by demonstrating the value of age-stratified economic evaluations. Countries with limited vaccine supply or constrained healthcare funding might adopt similar modeling frameworks to identify priority populations and deploy resources optimally, balancing public health impact with fiscal responsibility.
The communication of these findings is timely, coinciding with policy decisions around the roll-out of the 2023 to 2024 season’s mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. The incorporation of economic evaluations into vaccine recommendation processes signifies a maturing stage of pandemic response that balances scientific, economic, and ethical considerations. Public acceptance of vaccination programs may also benefit from transparent communication about their cost-effectiveness and societal value.
Fundamentally, this study illustrates the critical role interdisciplinary research plays in the pandemic response, blending epidemiology, economics, demography, and behavioral science to produce actionable insights. As vaccination efforts evolve from emergency response to sustained public health intervention, such analyses will be indispensable for tailoring approaches that maintain protection, optimize costs, and mitigate COVID-19’s multifaceted impact.
In summary, this modeling study presents comprehensive evidence supporting the cost-effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination, especially in older adults, with notable variability in younger populations that merits ongoing analysis. The results reinforce current immunization recommendations and emphasize the necessity of continual reappraisal as pandemic dynamics and scientific understanding evolve. This research exemplifies how data-driven strategies can inform equitable and economically sustainable vaccination policies central to long-term COVID-19 management.
Subject of Research: Economic Evaluation of COVID-19 Vaccination by Age Group Using Modeling Approaches
Article Title: Cost-Effectiveness of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination Across Age Groups in the United States: A Modeling Study
News Publication Date: Not specified
References: (doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.23688)
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccines, Adults, United States population, Modeling, Education, Young people, Age groups, Immunization, Cost effectiveness, Older adults, mRNA vaccines