Credit: GREEN ENERGY AND INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION
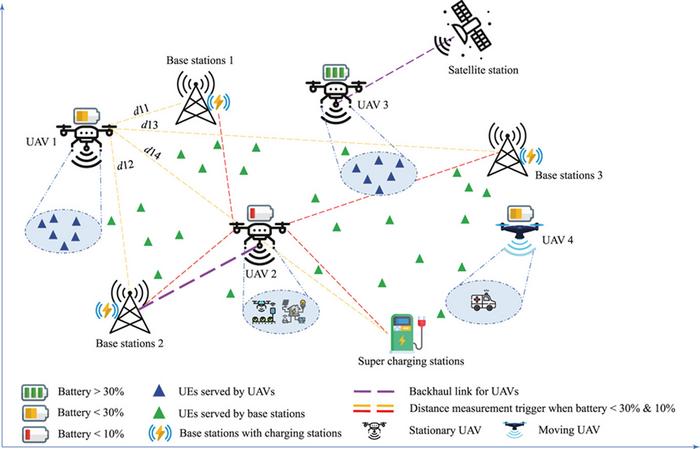
In the ever-evolving landscape of wireless communication, UAVs play a pivotal role, especially in rural, remote, and disaster-struck areas where traditional network infrastructure is absent. The GREENSKY model optimizes UAV charging behavior between static ground base stations and mobile supercharging stations, enhancing energy use and enabling longer operational periods without frequent recharging.
By integrating Mixed Integer Linear Programming, the GREENSKY model optimizes the recharging and routing processes for UAVs, thereby maximizing flight duration while minimizing energy consumption. The model strategically uses existing cellular base stations as opportunistic charging points, significantly reducing travel distances to recharge and ensuring UAVs can operate longer with less energy. Results show that GREENSKY achieves a significant reduction in energy consumption—9.1% less than traditional heuristic solutions.
Lead researcher Pratik Thantharate explains, “Our model is designed to make UAV networks more sustainable and efficient. By optimizing how and where UAVs recharge, we can extend their operational time dramatically, which is crucial for continuous and reliable service in critical areas.”
The development of this optimization model not only increases the efficiency of UAV networks but also pushes forward the innovation in energy management for UAVs serving as aerial base stations.This approach not only promises enhanced connectivity for underserved regions but also paves the way for smarter, energy-conscious technology deployments in 5G and beyond.
As UAVs become more embedded in various industries, the introduction of the GREENSKY model offers a more efficient, cost-effective approach to UAV energy management and task execution. The implications of the GREENSKY model extend beyond improved service reliability. By effectively leveraging both static and mobile charging stations, the model facilitates a smarter and more robust framework for future aerial communication networks. This approach not only promises enhanced connectivity for underserved regions but also paves the way for smarter, energy-conscious technology deployments in 5G and beyond.
References
Authors: Pratik Thantharate, Anurag Thantharate, Atul Kulkarni
Affiliation: School of Computing and Engineering, University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO, USA
Title of original paper: Innovative GREENSKY Model Elevates UAV Efficiency in Next-Gen Wireless Networks
Journal: Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation
DOI: 10.1016/j.geits.2023.100130
Journal
Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
GREENSKY: A fair energy-aware optimization model for UAVs in next-generation wireless networks
Article Publication Date
6-Jan-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.