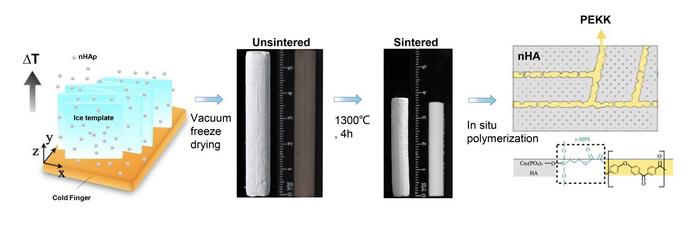
Nano hydroxyapatite (nHA), the primary inorganic component of bone widely utilized in bone tissue engineering, suffers from poor mechanical properties when used alone. Conversely, polyetherketoneketone (PEKK), a high-performance polymer approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and used in dentistry and biomaterial science, struggles with bioinertia, affecting its osteogenesis applications.

Credit: ZHONGYI WANG
Nano hydroxyapatite (nHA), the primary inorganic component of bone widely utilized in bone tissue engineering, suffers from poor mechanical properties when used alone. Conversely, polyetherketoneketone (PEKK), a high-performance polymer approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and used in dentistry and biomaterial science, struggles with bioinertia, affecting its osteogenesis applications.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Supramolecular Materials, researchers from Sichuan University, China, introduced pDA-nHA/PEKK composites that combine high strength and bioactivity.
“The optimal combination of nHA and PEKK can achieve higher mechanical property and bioactivity,” shares lead author Zhongyi Wang. “Nevertheless, conventional melt blending techniques often result in weakened strength due to nanoparticle agglomeration and the lack of chemical bonds between the inorganic and organic constituents.”
To that end, the team drew inspiration from the structure of cortical bone. By employing freeze-casting technology, the researchers mimicked the bone’s hierarchical structure, which is known for its exceptional stiffness and toughness. This technique allowed them to produce complex hierarchical materials. The novel approach, characterized by the in-situ polymerization of PEKK, resulted in the development of pDA-nHA scaffolds with enhanced osteo-inductive abilities and supplemented mechanical strength through PEKK.
Corresponding Haiyang Yu highlighted this development as an advancement in supramolecular materials, surpassing the strength capabilities of current methods. Yu hopes their approach to hierarchical architecture and in-situ polymerization will inspire further scientific discoveries.
###
Contact the author: Haiyang Yu, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610041, China yhyang6812@scu.edu.cn
Qiang Wei, College of Polymer Science and Engineering State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials and Engineering Sichuan University Chengdu, Sichuan 610065, China wei@scu.edu.cn
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Supramolecular Materials
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Fabrication of the polyetherketoneketone-reinforced nano-hydroxyapatite composites as inspired by the cortical bone
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.