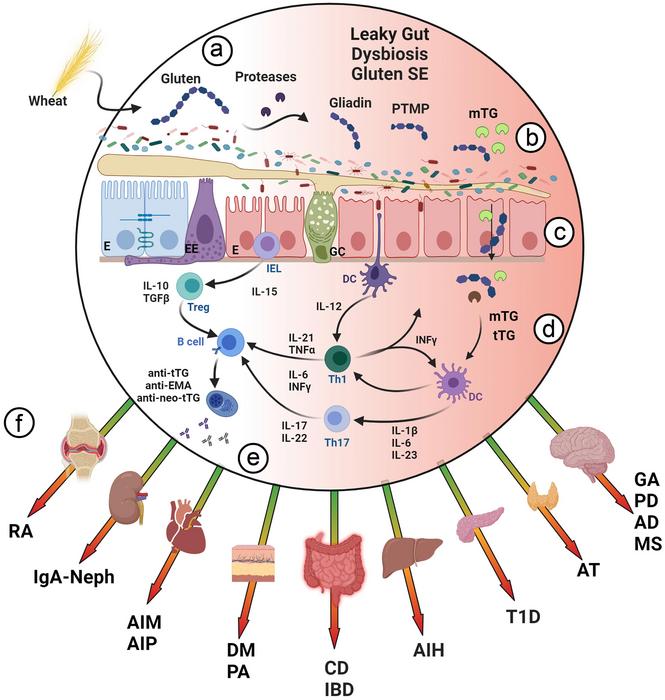
The interaction between humans and their environment, mediated by nutrition, plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses. Chronic inflammatory diseases have been on the rise, and the scientific community has been actively exploring pro-inflammatory nutrients as potential therapeutic targets. Gluten, a major component of wheat, barley, and rye, has been implicated in numerous health issues, particularly celiac disease (CD). This review essay summarizes the key findings of a recent study published in the Journal of Translational Gastroenterology, focusing on the proinflammatory effects of gluten and its implications in autoimmunity.

Credit: Aaron Lerner, Carina Benzvi, Aristo Vojdani
The interaction between humans and their environment, mediated by nutrition, plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses. Chronic inflammatory diseases have been on the rise, and the scientific community has been actively exploring pro-inflammatory nutrients as potential therapeutic targets. Gluten, a major component of wheat, barley, and rye, has been implicated in numerous health issues, particularly celiac disease (CD). This review essay summarizes the key findings of a recent study published in the Journal of Translational Gastroenterology, focusing on the proinflammatory effects of gluten and its implications in autoimmunity.
Gluten and Its Components
Gluten is a complex protein mixture consisting primarily of glutenin and gliadin. Gliadin, comprising about 70% of gluten, is particularly relevant in inducing harmful immune responses in CD. Gluten is abundant in the Western diet and can lead to various adverse effects beyond CD, suggesting its broader role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Gluten-Induced Inflammation in Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a chronic, autoimmune, inflammatory disorder characterized by intestinal injury, activated immune systems, and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines. Gluten, specifically gliadin peptides, acts as the trigger for this disease. Gliadin peptides induce mucosal inflammation, epithelial damage, and intestinal dysbiosis. Successful gluten withdrawal ameliorates these inflammatory features, underscoring the crucial role of gluten in CD pathogenesis.
Beyond Celiac Disease: Gluten and Other Autoimmune Diseases
The harmful effects of gluten extend beyond CD, affecting multiple body compartments and organs. Gluten peptides can compromise gut permeability, allowing immunogenic molecules to reach internal compartments and trigger autoimmune responses in remote organs. The distribution of gliadin peptides to these organs leads to organ dysfunction and pathology through post-translational modifications, which turn naïve peptides into immunogenic and proinflammatory molecules. This gluten-mediated inflammatory cascade is thought to be involved in a range of autoimmune diseases, including dermatitis herpetiformis, gluten ataxia, gluten allergy, and potentially other non-celiac autoinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions.
The Place of Gluten in Human Nutrition
Despite its proinflammatory properties, gluten has long been a staple in human nutrition, providing dietary fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. However, gluten does not contribute essential nutrients, and its avoidance does not compromise human well-being except in well-defined gluten-dependent conditions. The increasing popularity of gluten-free diets, driven by pseudoscientific claims, has significantly impacted dietary habits. However, a gluten-free Mediterranean diet, combining the benefits of both approaches, may be a healthier alternative.
Gluten Side Effects and Pathogenesis
Gluten has multiple side effects, including proinflammatory and pro-oxidative activities, which lead to gut dysfunction and inadequate health outcomes. Gliadin peptides can induce cellular stress, activate proliferative mechanisms, trigger a pro-inflammatory storm, and inhibit critical ion channels and vesicular trafficking. Furthermore, gluten-related changes in gut microbiota and enhanced enzymatic modifications can lead to autoimmunity induction through molecular mimicry.
Conclusions
Gluten, as a proinflammatory molecule, plays a crucial role in celiac disease and potentially other autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. The identification of gluten’s harmful effects highlights the need for a comprehensive investigation into its role in non-celiac autoimmune conditions. Gluten withdrawal can alleviate disease activity in CD and potentially other chronic inflammatory, metabolic, and autoimmune disorders. While gluten avoidance may be beneficial in gluten-dependent conditions, a gluten-free Mediterranean diet is recommended to ensure overall nutritional adequacy.
This review summarizes the key findings of the recent study on gluten’s proinflammatory effects and their implications in autoimmune diseases, providing insights into the mechanisms underlying gluten-mediated inflammation and potential therapeutic avenues.
Full text
The study was recently published in the Journal of Translational Gastroenterology.
Journal of Translational Gastroenterology (JTG) dedicates to improving clinical diagnosis and treatment, advancing understanding of the molecular mechanisms, and promoting translation from bench to bedside of gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, and pancreatic diseases. The aim of JTG is to provide a forum for the exchange of ideas and concepts on basic, translational, and clinical aspects of gastroenterology, and promote cross-disciplinary research and collaboration.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Journal of Translational Gastroenterology
Article Title
Gluten is a Proinflammatory Inducer of Autoimmunity
Article Publication Date
28-Jun-2024