Esophageal cancer, a highly aggressive malignancy originating in the esophageal epithelium, poses significant public health challenges in China, where it ranks sixth in incidence and fifth in mortality among cancers. The country’s large population contributes to over half of the global cases and deaths from esophageal cancer. This cancer’s poor prognosis is often due to late diagnosis, as early-stage esophageal cancer is typically asymptomatic, leading to diagnoses at more advanced stages. The geographical distribution of high-risk areas in China, such as the southern side of the Taihang Mountains, the Dabie Mountains, and northern Sichuan, underscores the need for focused screening efforts. Since 2005, China’s national public health initiatives have emphasized endoscopic screening in over 110 high-risk areas, yielding significant outcomes, although the overall decline in incidence and mortality rates remains gradual.

Credit: Ruihua Shi,
Esophageal cancer, a highly aggressive malignancy originating in the esophageal epithelium, poses significant public health challenges in China, where it ranks sixth in incidence and fifth in mortality among cancers. The country’s large population contributes to over half of the global cases and deaths from esophageal cancer. This cancer’s poor prognosis is often due to late diagnosis, as early-stage esophageal cancer is typically asymptomatic, leading to diagnoses at more advanced stages. The geographical distribution of high-risk areas in China, such as the southern side of the Taihang Mountains, the Dabie Mountains, and northern Sichuan, underscores the need for focused screening efforts. Since 2005, China’s national public health initiatives have emphasized endoscopic screening in over 110 high-risk areas, yielding significant outcomes, although the overall decline in incidence and mortality rates remains gradual.
Goals of Screening for Esophageal Cancer
The primary goal of esophageal cancer screening is early detection, particularly of early-stage cancer or esophageal intraepithelial neoplasia. Early identification facilitates timely intervention and treatment, significantly improving patient survival rates and quality of life. Research indicates that early diagnosis can increase the five-year survival rate to over 95%, demonstrating the critical importance of screening. Screening programs have been shown to reduce the incidence and mortality rates of upper gastrointestinal cancers significantly, underscoring the potential benefits of early detection.
Risk Factors and Screening Target Population
In China, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the predominant type of esophageal cancer, with several risk factors contributing to its incidence. These include smoking, alcohol consumption, consumption of hot or red foods, poor oral hygiene, and insufficient intake of fresh fruits and vegetables. Additional factors such as family history, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, gastric mucosal atrophy, and a history of head and neck SCC further increase the risk. Although esophageal adenocarcinoma is less common in China, it is associated with risk factors like smoking, obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Barrett’s esophagus. Given these risk factors and China’s demographic profile, screening is recommended for individuals aged forty and above, particularly those in high-incidence areas or with specific high-risk characteristics.
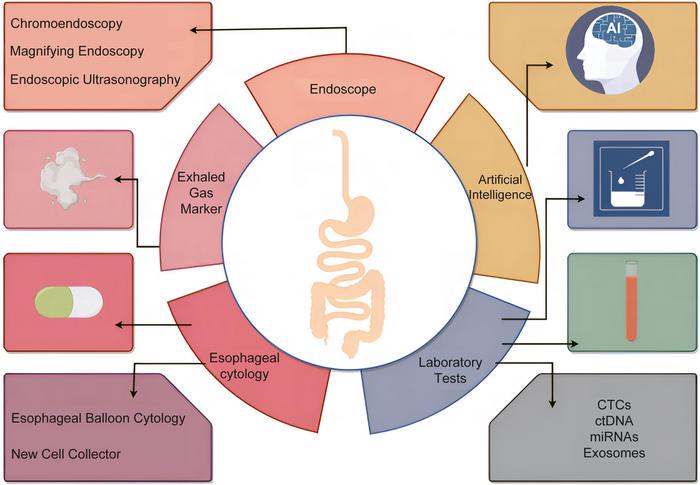
Current Status of Screening Methods
Current screening methods for esophageal cancer in China include endoscopy, exfoliative cytology, and biomarker detection. Traditional endoscopic techniques, such as white-light endoscopy, have been the mainstay of screening. However, advanced technologies like chromoendoscopy, magnifying endoscopy, and endoscopic ultrasound are gaining traction. These techniques offer enhanced visualization of mucosal surfaces and can improve the accuracy of early cancer detection. Despite their advantages, these methods are not widely adopted at the grassroots level due to high costs and technical complexities.
Emerging Technologies and Future Directions
Innovations in esophageal cancer screening include artificial intelligence-assisted methods, which enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis. The use of artificial intelligence in analyzing cytological samples collected by advanced esophageal cell collectors represents a significant improvement over traditional methods. Additionally, new endoscopic technologies, such as magnetic capsule endoscopy and confocal laser microscopy, are being explored for their potential to improve patient comfort and screening accuracy. However, these technologies are currently limited by high costs and a lack of comprehensive prospective studies.
Conclusions
Esophageal cancer remains a major public health concern in China, necessitating effective screening strategies. The continuous development and implementation of advanced screening technologies are crucial for improving early detection rates and patient outcomes. With ongoing advancements and reduced research and development costs, these new technologies are expected to become more widely accessible, providing more efficient and convenient screening options for esophageal cancer in China.
Full text
The study was recently published in the Cancer Screening and Prevention.
Cancer Screening and Prevention (CSP) publishes high-quality research and review articles related to cancer screening and prevention. It aims to provide a platform for studies that develop innovative and creative strategies and precise models for screening, early detection, and prevention of various cancers. Studies on the integration of precision cancer prevention multiomics where cancer screening, early detection and prevention regimens can precisely reflect the risk of cancer from dissected genomic and environmental parameters are particularly welcome.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Cancer Screening and Prevention
Article Title
The Current Status and Prospects of Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Cancer in China
Article Publication Date
25-Jun-2024