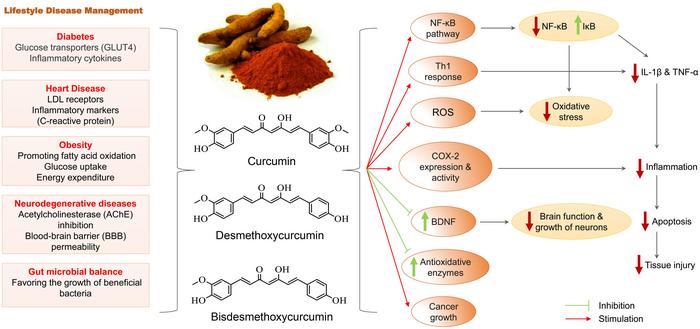
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), have emerged as a major health burden globally, including in India. These diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and stress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs are responsible for 41 million deaths annually, accounting for 74% of all global deaths. Notably, 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.

Credit: Anuradha Singh
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), have emerged as a major health burden globally, including in India. These diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and stress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs are responsible for 41 million deaths annually, accounting for 74% of all global deaths. Notably, 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
The increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases poses a significant challenge to public health systems. While modern medicine offers effective treatments, there are research gaps in areas such as long-term management, addressing the root causes of unhealthy lifestyles, and minimizing side effects. This highlights the necessity for complementary and integrative approaches that combine conventional medicine with evidence-based natural therapies. One promising avenue is the use of herbal-based nutraceuticals, which offer potential benefits for managing lifestyle diseases. However, further research is crucial to establish their efficacy, safety, and optimal dosages for specific conditions.
Herbal-based Nutraceuticals: A Potential Solution?
Herbal-based nutraceuticals are natural products derived from plants, offering various health benefits beyond basic nutrition. They often contain bioactive compounds from plants traditionally used in Ayurveda, Siddha, and other systems of medicine in India. These traditional medical systems are valuable resources for rural populations due to their accessibility and perceived lower side effects compared to modern pharmaceuticals. This has contributed to a global resurgence of interest in traditional medicine, including Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Siddha, and Unani.
The Ayurvedic medicine market in India is estimated to be worth INR 50 billion (USD 6.25 billion) in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15-20% over the next five years. Factors driving this growth include increasing awareness of Ayurvedic medicine benefits, rising disposable incomes, and the growing prevalence of lifestyle diseases. The Indian government supports the Ayurvedic medicine industry, promoting its growth through initiatives like the National Mission on Ayurveda, Yoga, and Naturopathy. Despite the popularity of herbal-based nutraceuticals, there is a critical need to evaluate their efficacy and safety in managing lifestyle diseases through empirical studies.
Growing Awareness and Consumption
The Indian population has undergone a drastic shift in lifestyle, leading to a noticeable growth in health consciousness. This has created a favorable environment for the acceptance and adoption of herbal-based nutraceuticals as practical and cost-effective solutions. Indian consumers are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of these natural remedies, leading to a surge in their popularity and consumption. This shift reflects a growing awareness of the benefits of natural remedies and the desire for alternative approaches to health management.
Despite the widespread use of herbal-based nutraceuticals, it is important to choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands. Herbal-based nutraceuticals can interact with other medications, so it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking them. They are not a substitute for a healthy diet and lifestyle, which include eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress effectively.
Conclusions
India boasts a rich tradition of utilizing herbal remedies for various ailments, with knowledge and practices passed down through generations. Compared to conventional medications, herbal remedies are often readily available and affordable, particularly in rural areas with limited healthcare access. Many herbal remedies are perceived to have fewer side effects compared to pharmaceutical drugs, making them attractive to individuals seeking natural solutions.
Despite numerous studies on herbal remedies, many lack robust methodologies and rigorous scientific standards, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about their efficacy. Standardization of herbal products remains a significant concern due to variations in potency, purity, and processing. Collaborative research bridging traditional knowledge and modern science can pave the way for developing effective and sustainable therapies. Enhancing public awareness about the potential benefits and limitations of these remedies is essential for responsible use and informed decision-making. By exploring herbal-based nutraceuticals alongside established medical practices, we can move towards a more holistic and sustainable approach to managing lifestyle diseases in India, paving the way for a healthier and brighter future.
Full text:
The study was recently published in the Future Integrative Medicine.
Future Integrative Medicine (FIM) publishes both basic and clinical research, including but not limited to randomized controlled trials, intervention studies, cohort studies, observational studies, qualitative and mixed method studies, animal studies, and systematic reviews.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Future Integrative Medicine
Article Title
Herbal-based Nutraceuticals in Management of Lifestyle Diseases: Experience from Indian Population
Article Publication Date
20-Jun-2024